intro
Let’s learn how to use DDL statements to change the structure of a database.
Adding new tables, indexes, and triggers and updating existing ones are all common operations performed by database administrators. These tasks impact the database schema, and the queries behind them belong to SQL DDL. But what does that mean?
In this guide, you will see what DDL stands for, how it is related to other SQL languages, and how to use it to manipulate database objects.
Let's dive in!
What Is DDL In SQL?
In SQL, DDL stands for “Data Definition Language” and represents the syntax for describing the database schema. In detail, DDL consists of SQL commands to create and update database objects, such as tables, indexes, views, stored procedures, and triggers.
The DDL commands in SQL are:
Note that SQL dialects may have some unique DDL commands. For example, MySQL has the RENAME statement to change the name of existing tables. Similarly, PostgreSQL and Oracle offer the COMMENT command to add or update a comment about a database object.
As you can notice, all DDL SQL statement allows you to change the database structure, but not the data. To add or update data from a database, you need to the CRUD commands offered by DML (Data Manipulation Language).
SQL DDL vs DML vs DQL vs DCL vs TCL
The SQL commands can be categorized into the following categories:
Now that you know the different SQL languages available and their differences, it is time to delve deeper into the SQL DDL commands!
SQL DDL Commands
In this section, you will explore the DDL statements in SQL: CREATE, ALTER, DROP, and TRUNCATE. For each command, you will see details on its syntax, how to use it, and a real-world example. Since DDL commands modify the structure of a database, it is essential to have a tool that simplifies the process of exploring their effects. This is where DbVisualizer comes into play!
As a comprehensive database client, DbVisualizer enables you to visually explore databases across a wide range of DBMS technologies. Here, you will use it to execute queries involving those DDL SQL commands. Keep in mind that DbVisualizer provides user-friendly modals and buttons to perform DDL operations in a simplified way, making database management more accessible.
The following examples will be in MySQL, but the queries below will work in any other SQL-based DBMS. Let’s explore DDL commands in SQL!
CREATE
The CREATE statement is used to create new database objects, such as tables, views, or indexes. The syntax of the SQL DDL command changes based on the object to create. To add a new table to the database, the syntax is:
1
CREATE TABLE <table_name> (
2
<column_1> <sql_datatype>,
3
<column_2> <sql_datatype>,
4
...
5
<column_N> <sql_datatype>,
6
);
For example, you can use a CREATE query to add an employees table to the company database as below:
1
CREATE TABLE employees (
2
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
3
first_name VARCHAR(50),
4
last_name VARCHAR(50),
5
hire_date DATE
6
);
A new table will be added to the database as desired:

Given a specific table, some useful information to get is the DDL command used to create it. Retrieving that info in DbVisualizer is very simple. All you have to do is open the table in a new tab by clicking on it and selecting the “DDL” tab:
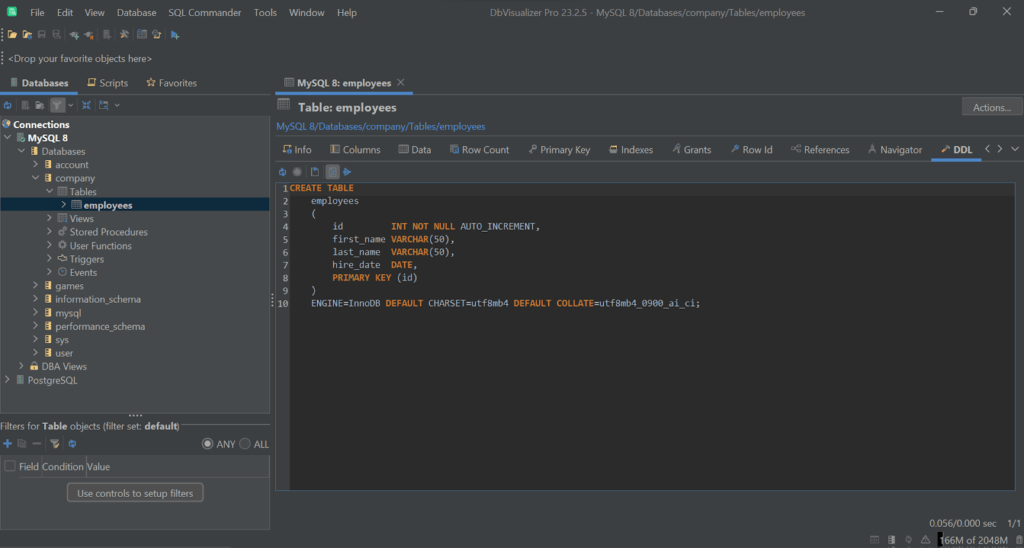
You can then copy the query and use it to create a similar table on the database. Otherwise, you could create a table like another table with the special CREATE ... LIKE syntax.
ALTER
The ALTER command modifies an existing database object's structure, such as adding, changing, or deleting columns from a table. Other use cases include renaming database objects or updating the logic of an index, stored procedure, or trigger.
The syntax of the SQL DDL statement changes based on the operation to be performed. For adding a new column to an existing table, the syntax is:
1
ALTER TABLE <table_name>
2
ADD <column_name> <sql_datatype>;
For instance, you can use an ALTER statement to add the department_id column to the employees as follows:
1
ALTER TABLE employees
2
ADD department_id INT;

As you can visually verify in DbVisualizer in just a couple of clicks, employees will now have a new column:

Its DDL definition will be updated accordingly:
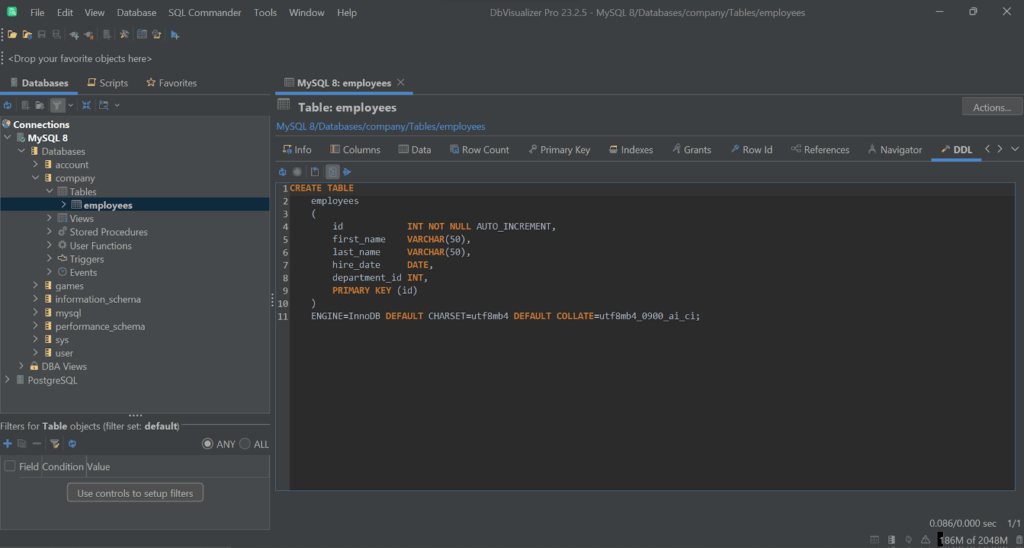
Note the department_id definition in the CREATE TABLE query.
DROP
The DROP statement removes a database object entirely. It is typically used to delete tables, views, indexes, or other objects from the database. The syntax to drop a table is:
1
DROP TABLE <table_name>;
For example, launch the following query to delete the employees table:
1
DROP TABLE employees;

Refresh the database connection and notice that the company database no longer has an employees table:
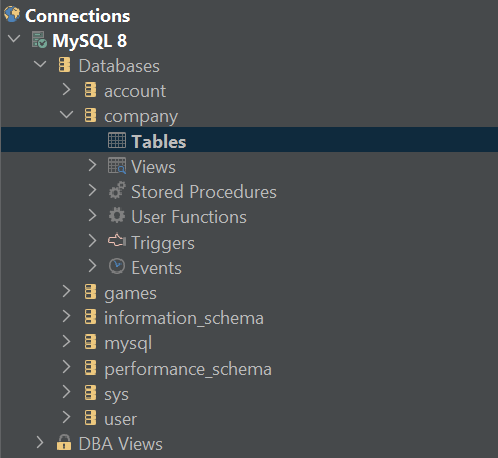
TRUNCATE
The TRUNCATE statement removes all the data from a table while retaining the table structure. It is a faster alternative to deleting all records one by one. Its syntax is simple:
1
TRUNCATE [TABLE] <table_name>;
For example, you can clear all records from the employees table in MySQL with:
1
TRUNCATE TABLE employees;
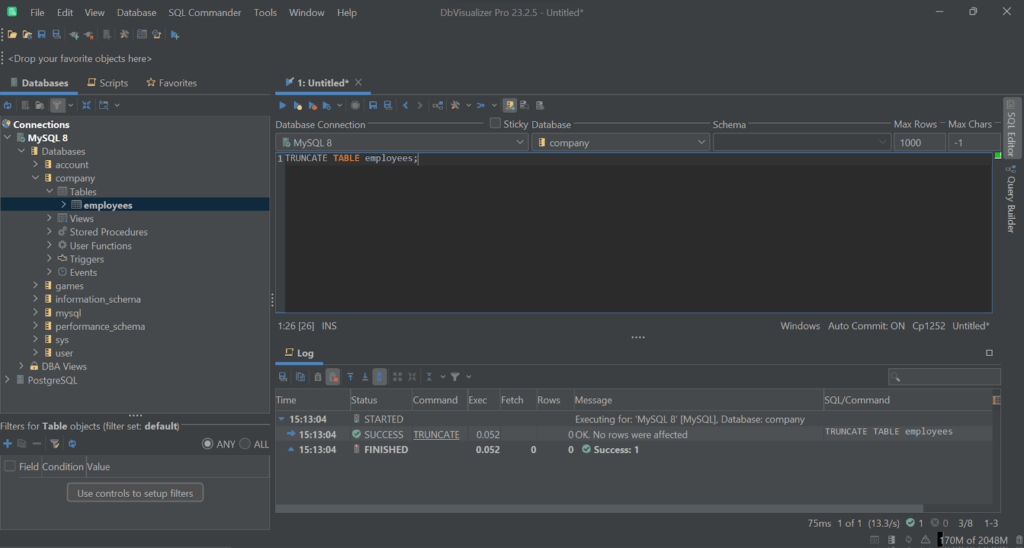
The employees table will now contain 0 records:

Et voilà! You are now a SQL DDL expert!
Conclusion
In this article, you dug into the SQL data definition language. You started from the main concepts and then explored each DDL command. You now know:
DDL is about changing the structure of a database. Keep track of that with a visual database client like DbVisualizer. On top of supporting dozens of databases, the tool comes with ER schema representation functionality, a drag-and-drop UI to build queries, and powerful query optimization capabilities. Try DbVisualizer for free now!
FAQ
What are the SQL DDL statements?
SQL DDL statements are used to define and manage the structure of a database. These commands include:
DDL statements in SQL focus on the database's schema, ensuring its organization and integrity.
What is the difference between SQL DDL and sql.dll?
DDL refers to Data Definition Language or Data Description Language, which consists of commands for defining the structure of a database. On the other hand, sql.dll is a Windows dynamic-link library file used by some software applications. These are entirely different concepts: DDL is a category of SQL commands, while sql.dll is a file used for software functionality.
What are the key aspects to consider in the DDL vs DML SQL comparison?
In a DDL vs DML comparison, key aspects to consider are their purposes. DDL focuses on defining and modifying the database structure, such as creating or altering tables. DML deals instead with manipulating data within tables, including inserting, updating, and deleting records. DDL changes the schema, while DML affects the actual data.
How to get the SQL DDL definition of a table?
To obtain the SQL DDL definition, you can use the SHOW CREATE TABLE statement with the syntax below:
1
SHOW CREATE TABLE <table_name>;
This query will provide the DDL definition of the specified table via a CREATE query. Otherwise, you can get that information with a couple of clicks in a powerful database client like DbVisualizer.
How to use DDL to prevent SQL injection?
To prevent SQL injection, you need to focus on the use of prepared statements, parameterized queries, and input validation in DDL statements. At the same time, keep in mind that most SQL injection attacks occur during data addition or update, so they are more related to DML statements. To prevent SQL injection, do not pass user input straight into a database without validation.