intro
Learn how to use the MySQL SUBSTRING_INDEX function through some real-world examples.
Learn how to use the MySQL SUBSTRING_INDEX function through some real-world examples.
String manipulation is such a common practice that most DBMS technologies expose functions to achieve both general and very specific goals. SUBSTRING_INDEX is one of them! This scenario-specific–yet extremely powerful–MySQL function enables you to perform string extraction with a single line of code. Is SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL? Or is it only available in MySQL?
Read this article and find that out! You will discover everything you need to know about SUBSTRING_INDEX, exploring its syntax, how it works, and its use cases.
Let's dive in!
What Is SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL?
SUBSTRING_INDEX is a MySQL function that returns a substring before a specified number of delimiter occurrences. This is not easy to understand at first, and it is better to see the function in action in an example. Consider the function call below:
1
SUBSTRING_INDEX('Hi! Hello, World!', '!', 1)
The output will be:
1
'Hi'
When changing the final argument from 1 to 2, the function call becomes:
1
SUBSTRING_INDEX('Hi! Hello, World!', '!', 2)
And the result will now be:
1
'Hi! Hello, World'
Basically, SUBSTRING_INDEX is like a virtual knife that slices a string. Your job is to say where it should stop slicing by specifying a special word or character and its occurrence index in the string.
How to Use the SUBSTRING_INDEX Function in MySQL
Here is the syntax of SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL, as supported by MySQL:
1
SUBSTRING_INDEX(str, delimiter, count)
In other words, the SUBSTRING_INDEX MySQL-specific function returns the substring from string str before/after count occurrences of the string delimiter. In particular, it retrieves the substring “before” count occurrences, when count is positive:
1
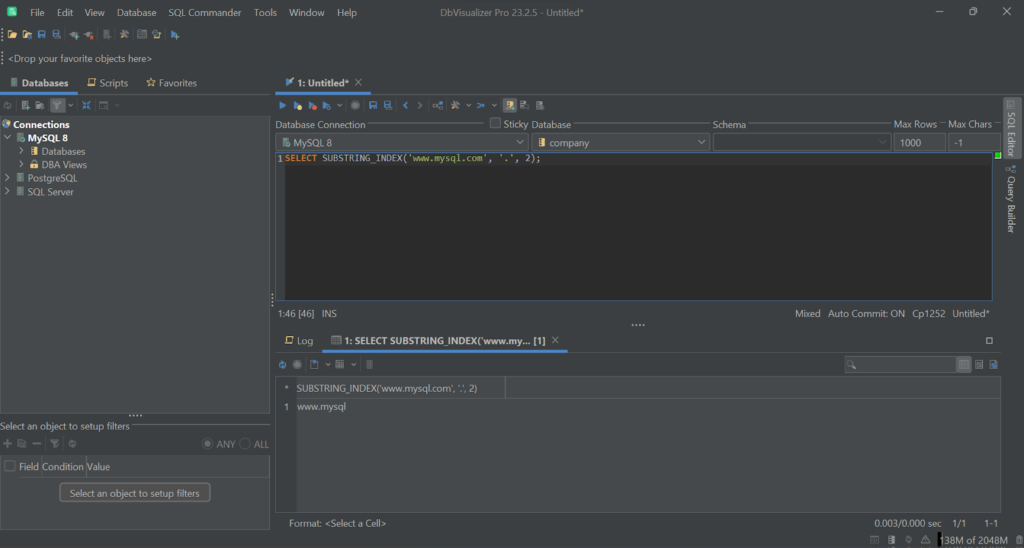
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('www.mysql.com', '.', 2); # 'www.mysql'
And “after” when count is negative:
1
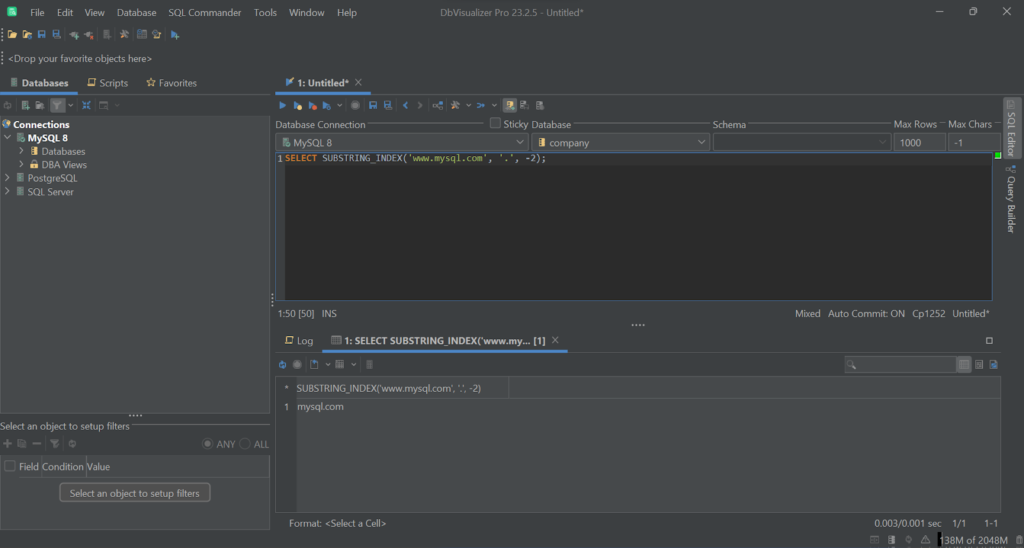
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('www.mysql.com', '.', -2); # 'mysql.com'
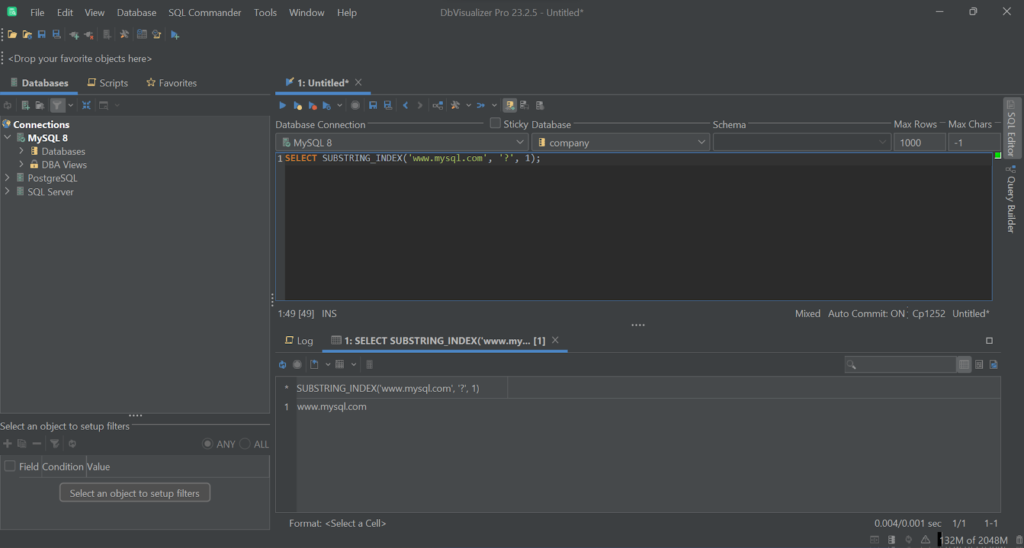
When delimiter does not appear in str, the function returns the original string:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('www.mysql.com', '?', 1); # 'www.mysql.com'
Similarly, if count is 0 or is greater than the number of occurrences in the string, it returns the original string:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('www.mysql.com', '.', 3); # 'www.mysql.com'

If delimiter is instead empty, SUBSTRING_INDEX returns an empty string:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING_INDEX('www.mysql.com', '', 1);

SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL: Use Cases
A guide to SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL would not be complete without some real-world use cases. Explore the most common ones!
Note: The queries in the examples below will be run in DbVisualizer, the database client
with the highest user satisfaction.
Extracting Domain from Email Addresses
Suppose you want to extract some data about users' favorite e-mail providers. This involves extracting the domain part (e.g., "example.com") from your users' e-mail addresses and counting them.
Here is how you can achieve that with SUBSTRING_INDEX in MySQL:
1
SELECT
2
SUBSTRING_INDEX(email, '@', -1) AS email_domain,
3
COUNT(*) AS email_domain_counter
4
FROM users
5
GROUP BY email_domain;
This query will retrieve the domain part after the "@" symbol from the email column in the users table, group by that, and count it:

Separating File Extensions from Filenames
Assume you have a file column in one of your tables, storing the name of some files. You want to separate the file extensions (e.g., ".pdf") from the filenames. Achieve that with the SUBSTRING_INDEX MySQL example query below:
1
SELECT file,
2
SUBSTRING_INDEX(file_path, '.', -1) AS file_extension
3
FROM reports;
That will produce the desired results:

Get Paths From URLs
Consider that you have a database with URLs and want to extract a specific part from them. For example, you want their domain. Instead of using a regular expression, you can concatenate two SUBSTRING_INDEX calls as follows:
1
SELECT url,
2
SUBSTRING_INDEX(SUBSTRING_INDEX(url, '://', -1), '/', 1) AS domain
3
FROM apis;
The query will first extract the part of the URL after the “://” characters. Then, it will select the part before the first “/” character, returning the desired URL domain data.

Wonderful! You now know how to adopt SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL to extract specific parts of strings!
Conclusion
In this guide to SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL, you learned what it is and how it works. This powerful MySQL string manipulation function helps you extract substrings based on a delimiter. The definition of the function is complex, but its use cases are very popular.
As the examples in this article demonstrate, you need a tool to visually explore query results to better appreciate the capabilities of the function. That is where a comprehensive database client such as DbVisualizer comes in! In addition to supporting several DBMSs, it offers advanced query optimization capabilities, ERD-type schema generation, and more. Try DbVisualizer for free today!
FAQ
Is SUBSTRING_INDEX part of the SQL standard?
SUBSTRING_INDEX is not part of the SQL standard. Instead, it is a string manipulation function available only in MySQL. Thus, do not expect SUBSTRING_INDEX to be available in other relational database management systems.
What is the SQL Server equivalent of SUBSTRING_INDEX?
The SQL Server equivalent of SUBSTRING_INDEX involves using a combination of functions like CHARINDEX, LEFT, and RIGHT to extract substrings based on delimiters. Keep in mind that there is not a direct equivalent function and achieving the same result may be tricky.
What is the SUBSTRING_INDEX PostgreSQL equivalent?
In PostgreSQL, you can achieve similar functionality to the MySQL SUBSTRING_INDEX function using a combination of string manipulation functions. You can use functions like POSITION, LEFT, and RIGHT to extract substrings based on delimiters, similar to how you would in SQL Server. Do not forget that there is no direct SUBSTRING_INDEX PostgreSQL equivalent.
What is the difference between SUBSTRING_INDEX and other string manipulation functions in SQL?
The main difference between SUBSTRING_INDEX and other string manipulation functions in MySQL, such as LEFT, RIGHT, and CONCATENATE, is that SUBSTRING_INDEX is specifically designed to extract substrings based on a specified delimiter. This makes it well-suited for tasks like splitting strings into parts or extracting portions before or after a delimiter. Other functions are more general-purpose and may require additional logic to achieve your specific goals.
Can SUBSTRING_INDEX handle cases where delimiters occur multiple times in a string?
Yes, SUBSTRING_INDEX in SQL can handle cases where delimiters occur multiple times in a string. It allows you to specify which occurrence of the delimiter to use when extracting the substring, making it versatile for handling various situations.