intro
This article aims to educate readers about the different types of data that can be stored in an Oracle database and how the database management tool DbVisualizer can be utilized to manage these data types. It will provide an overview of the various data types available in Oracle, including numerical, character, date and time, and large object database types.
The article will then demonstrate the steps to connect to an Oracle database using DbVisualizer, create table structures with different data types and insert data. The objective of this article is to help readers comprehend the importance of data types in an Oracle database and how to use DbVisualizer to manage them effectively.
Understanding Data Types in Oracle
A data type is a category that defines the type of values that a column can hold. In a database, a data type is a specification that determines the type of data that can be stored in a column of a table. This ensures that only the appropriate data type can be stored in the column.
Why are Data Types Important?
Data types are critical in any database management system as they ensure the accuracy of the data stored in the database and efficiency working with that data. Specifying the type of data that can be stored in a column helps prevent errors, save space, and improve performance. Properly choosing a data type makes it easier to understand and manage the data in our database instance.
How to Select the Correct Data Type?
Choosing the right data type involves considering factors such as the type of data, size of the data, performance requirements, portability needs, and potential future use of the data. By considering these factors, you can select a data type that best represents the type of data, helps optimize storage and retrieval performance, and accommodates any future requirements.
Datatypes in Oracle
Oracle, like many relational databases, offers a wide range of datatypes to store different kinds of data. To ensure the accuracy and efficiency of your queries, it is important to have a good understanding of the different datatypes in Oracle and to select the most suitable one for each column. The datatypes offered by Oracle are as follows:
1. Numerical Datatypes
Oracle offers several numerical datatypes, including NUMBER, INTEGER, and FLOAT. NUMBER is used to store numeric values with high precision, INTEGER is used to store whole numbers, and FLOAT is used to store approximate numeric values.
2. Character Datatypes
Oracle has 8 character datatypes CHAR, NCHAR, VARCHAR, VARCHAR2, and NVARCHAR, CLOB, NCLOB, and LONG. CHAR and VARCHAR2 are more important. VARCHAR2 is used to store variable-length character strings, while CHAR is used to store fixed-length character strings.
3. Date and Time Datatypes
Oracle provides two datatypes for date and time information: DATE and TIMESTAMP. DATE is used to store date and time information, and TIMESTAMP is used to store more precise date and time information.
4. Large Object Datatypes
Oracle has two datatypes for large objects, BLOB and CLOB. BLOB is used to store binary data, while CLOB is used to store character data.

If you are looking for an easy and powerful SQL client and database manager, then you've got to try DbVisualizer. It connects to nearly any database.
5. Raw Datatype
RAW is used to store variable-length binary data. It's often used for data that's not meant to be interpreted or manipulated, like encrypted information.
Overview of all oracle data types
The table below provides an overview of all the datatypes in Oracle.
| Data Type | Category | Description |
|---|---|---|
| NUMBER | Numeric | Used to store numeric values with high precision |
| INTEGERs | Numeric | Used to store whole number |
| FLOAT | Numeric | Used to store approximate numeric values |
| CHAR | Character | Used to store fixed-length character strings |
| NCHAR | Character | Used to store fixed-length national character set strings |
| VARCHAR2 | Character | Used to store variable-length character strings |
| NVARCHAR2 | Character | Used to store variable-length national character set strings |
| CLOB | Large Object | Used to store large character data |
| NCLOB | Large Object | Used to store large national character set data |
| LONG | Large Object | Used to store variable-length character data |
| BLOB | Large Object | Used to store binary data |
| DATE | Date and Time | Used to store date and time information |
| TIMESTAMP | Date and Time | Used to store more precise date and time information |
| RAW | Other | Used to store variable-length binary data |
Connecting and Managing Oracle Data Types with DbVisualizer
DBVisualizer can help Oracle users manage and query data types by providing information about data types, allowing data type conversion and validation, and querying data by data type. It provides a user-friendly interface for managing and querying data in the database. To visualize the integration of DbVisualizer with Oracle, we have to follow a few steps discussed below.
1. Download and Install DbVisualizer
First go to the following website link and download DbVisualizer. https://www.dbvis.com/download/
For the DbVisualizer setup, we need to install the JDK 17 first, so download JDK 17 from the official Oracle website. Make sure to download the package applicable to your operating system.

After downloading JDK, install it and verify to figure out the version of JDK using the following command in your CLI.

1
java -version
Now open the downloaded “.exe” file and install DbVisualizer.
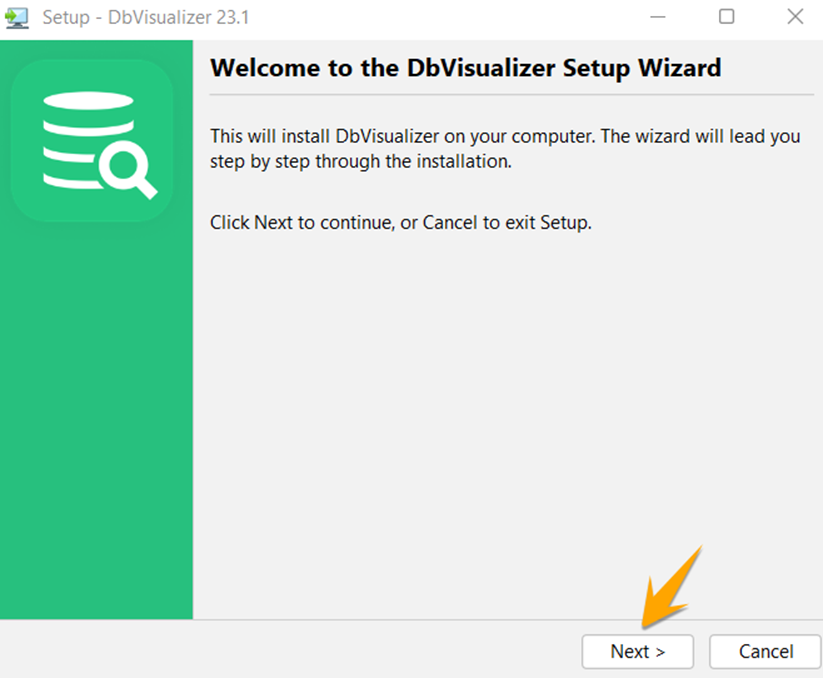
Select the right directory for installation.
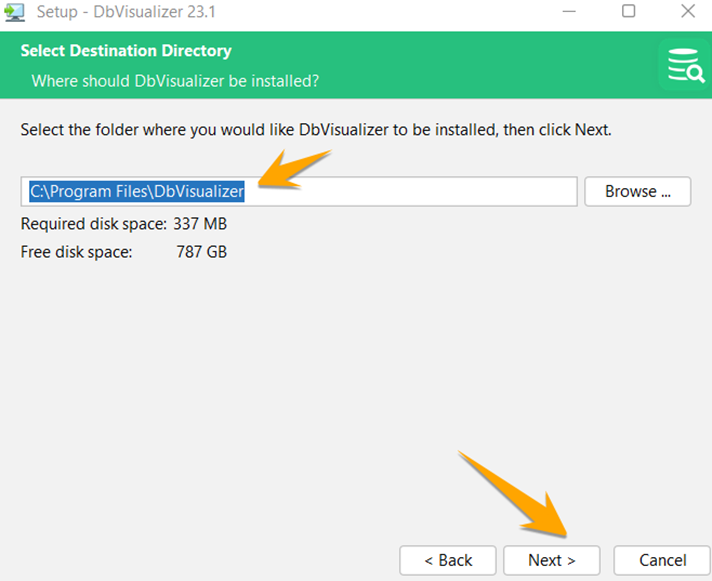
Check mark the DbVisualizer SQL file option if you want DbVisualizer to open all SQL files in the future, and click on the “Next” button.

Select if you want to create a desktop icon and press the “Next” button.
The installation will start - let it finish before performing any additional steps.
Now click on the “Finish” button and run the DbVisualizer.
DbVisualizer has been successfully installed.
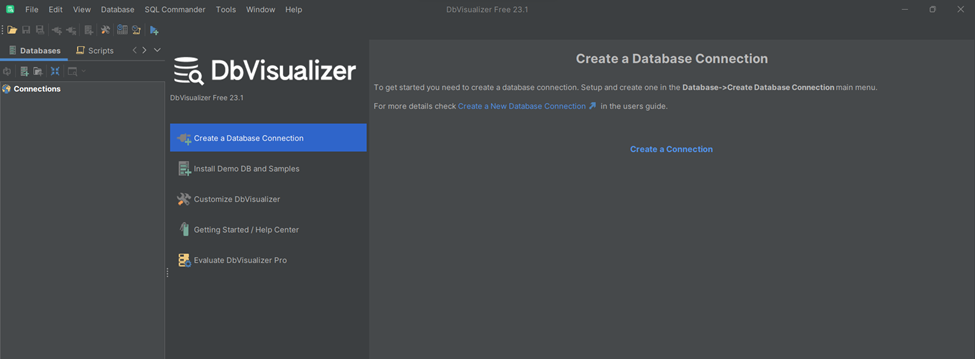
2. Download and Install the Oracle Database
Go to this URL and download the Oracle database.
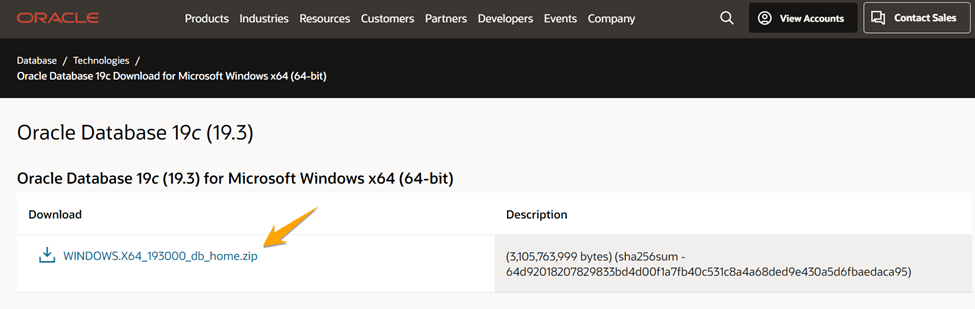
Now extract the downloaded .zip file.
Open the extracted folder and right click on the “setup.exe” and run it as an administrator.

Select the marked checkbox and click “Next.”

Now select the “Desktop Class” and press “Next”.

Choose the “Create New Windows User” option. Write the username and password of your choice and click “Next.”
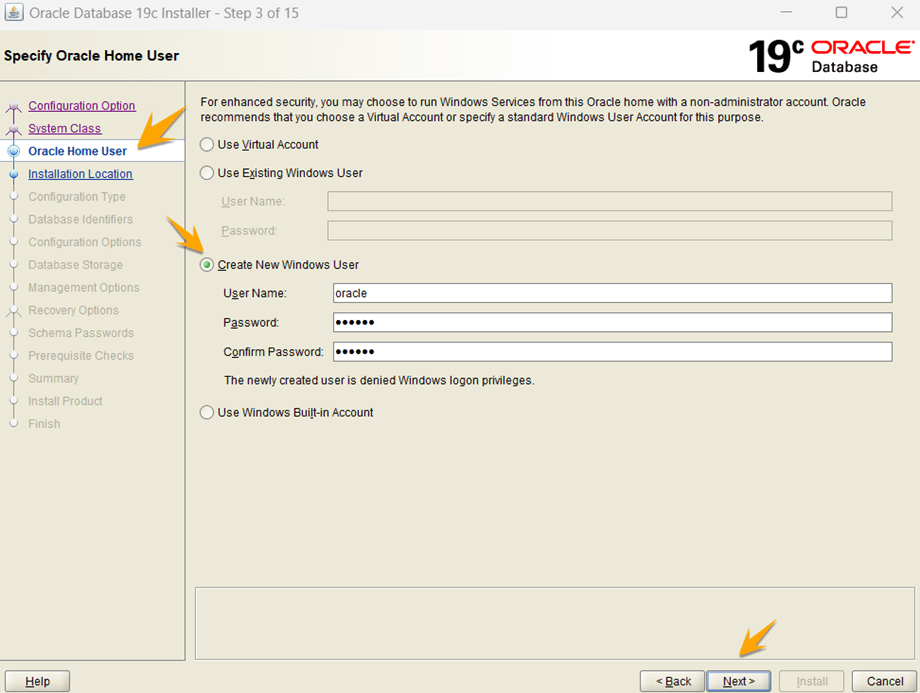
Select the location for database installation, provide further credentials, and press “Next.”
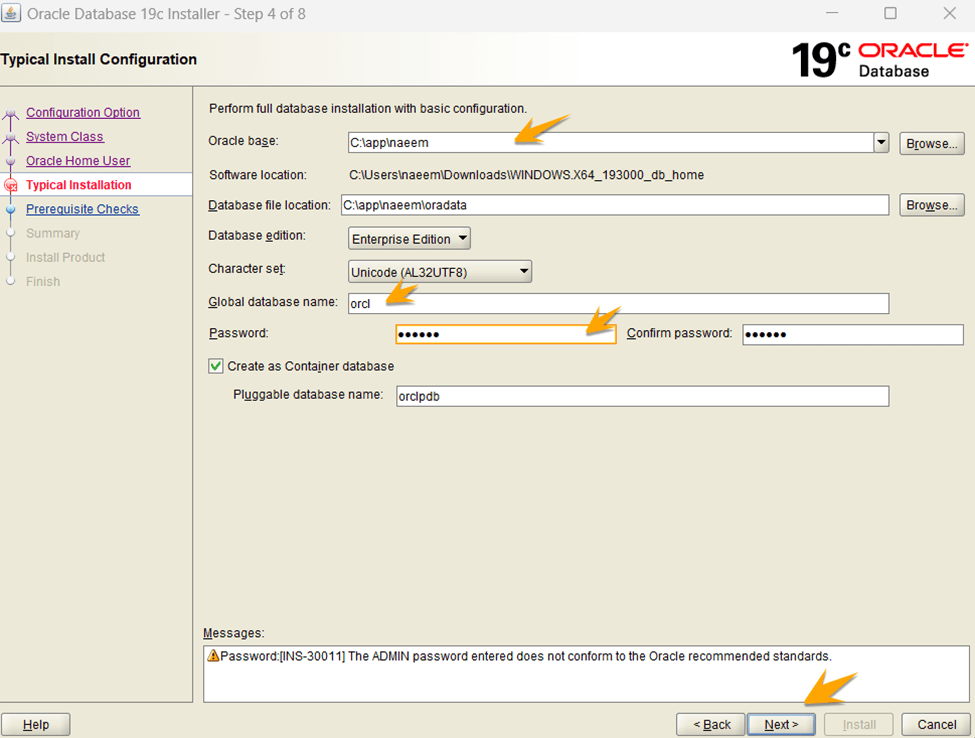
Now save the response file for the future usage and import of your settings and click on “Install.”

Installation is in process now.
Once the installation has been successfully completed, you can verify it using the URL mentioned below.

Once you reach the URL, you will see this screen. Provide the Username as “sys” and the password the same as what you have set for Oracle DB, and press the “Login” button.

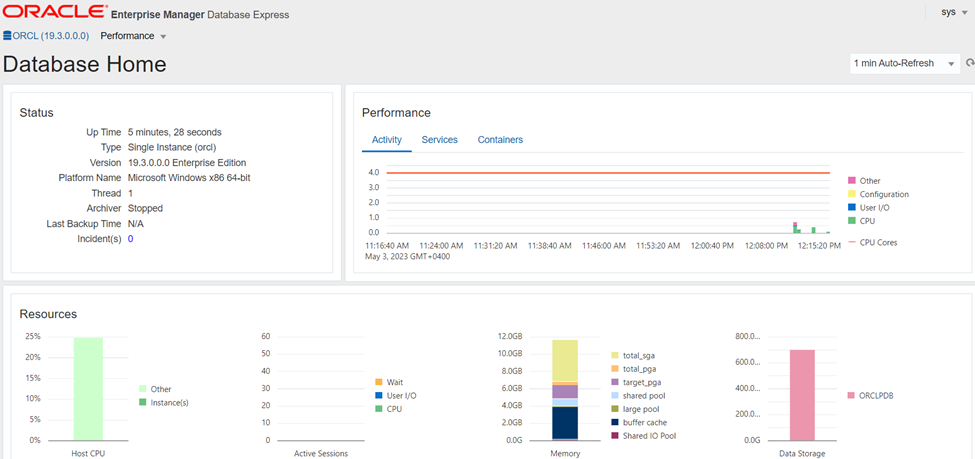
After logging in, you will see the Oracle dashboard.
3. Connecting to Oracle through DbVisualizer
Now we will create a new connection with the Oracle database by using DbVisualizer. Click on the highlighted plus icon and select the “Oracle 9i” option.

Now enter the username as “SYS” and Oracle DB password, choose the SYS Role as “SYSDBA”, and then click on the “Connect” button.

Now the connection has been established.

4. Working with Oracle Using DbVisualizer
Now we will create a table with multiple data types, insert data into it, and visualize everything with DbVisualizer.
Create Table and Add Columns
Click on the plus icon to open a new SQL command tab.

Now write a SQL query in which a “products” table will be created with multiple columns.

1
CREATE TABLE products (
2
productId INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
3
productName VARCHAR2(50) NOT NULL,
4
description VARCHAR2(2000),
5
price NUMBER(10, 2) NOT NULL,
6
quantity INTEGER NOT NULL,
7
image BLOB
8
);
Now verify that the table has been created by looking into the “SYS” schema.
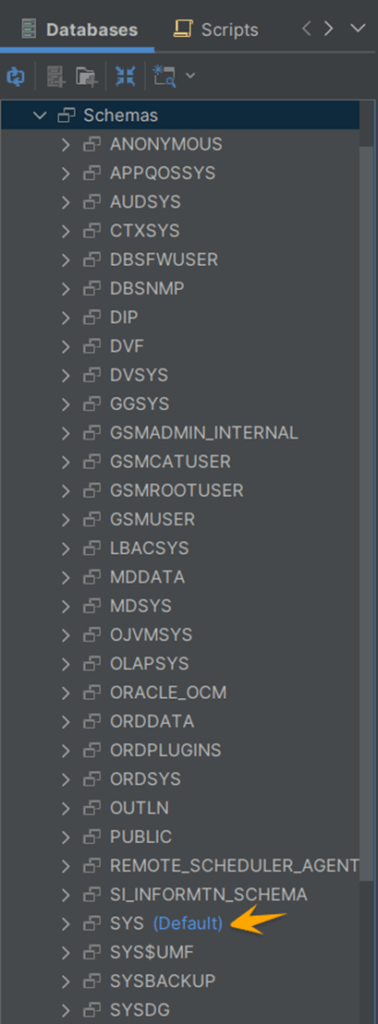
The table has been created successfully.

Data Insertion into Table Columns
Execute the following query to insert data into the table.

1
INSERT INTO products (productId, productName, description, price, quantity, image)
2
VALUES (1, 'Orange', 'Orange is sour and sweet fruit', 9.99, 10, NULL);
Data has been successfully inserted into the “products” table.

Conclusion
In conclusion, selecting the appropriate Oracle data types for each column is crucial for maintaining database performance. Using a database management tool such as DbVisualizer can simplify the process of working with datatypes in Oracle.
With its user-friendly interface, DbVisualizer allows for easy connections to an Oracle database, the creation of tables with different datatypes, insertion and retrieval of data, and can help you improve database security. By utilizing DbVisualizer, database administrators and developers can effectively manage their Oracle databases and ensure that data is stored and processed correctly.
Having a good understanding of datatypes in Oracle and utilizing DbVisualizer to simplify database management tasks can greatly enhance the performance and reliability of an Oracle database.
To learn more about database management and news from the database world, make sure to keep an eye out on our TheTable blog, and until next time.