intro
In today’s business world, data analysis is the lifeline of any business. To remain competitive, businesses and organizations must analyze data to understand market trends, customer behavior, and more.
To analyze data, you need the ability to write SQL queries. However, writing queries from scratch is time-consuming especially if you have limited coding experience. Fortunately, some tools enable you to generate SQL queries easily without needing to write them from scratch.
In this article, you will learn how to use an SQL client to automatically generate SQL queries.
Prerequisites
You need a SQL client and some database knowledge to follow through with this article. In this case, we will use Postgres as the database management system and DbVisualizer as the database SQL client.
To install PostgreSQL, navigate to the PostgreSQL download page and download it for your operating system. You can follow this guide to install PostgreSQL on Windows, this guide to install it on Linux, and this guide to install it on macOS.
To install DbVisualizer, navigate to the DbVisualizer download page. Then download the recommended installer for your operating system. Follow the user guide here to learn how to get started with DbVisualizer.
Connecting Postgres to DbVisualizer
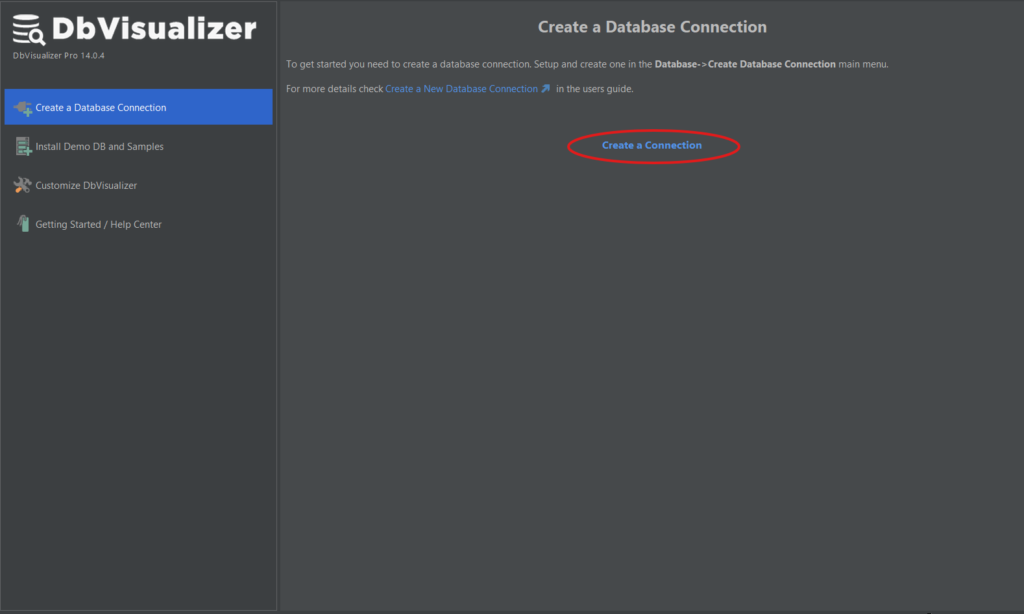
Step 1: Start DbVisualizer and click Create a Connection button as shown below.
Step 2: Search for and double-tap the Postgres driver from the popup menu on the left side of your screen, as shown below.

An object view tab for the Postgres connection is opened.

Step 3: Fill in the database connection name field with “PostgresQueryBuilder,” as shown below.

Fill in the Database Userid field with “postgres” and the Database Password field with your password (we use “test123”) as shown below.
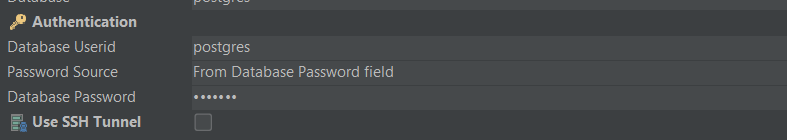
Once done, click the Connect button at the bottom, and if there are any issues, they will be displayed under the Connection Message section.

If the connection is successful, you should see the newly created PostgresQueryBuilder connection on the left sidebar of your screen.
Importing Data Into a PostgreSQL Database
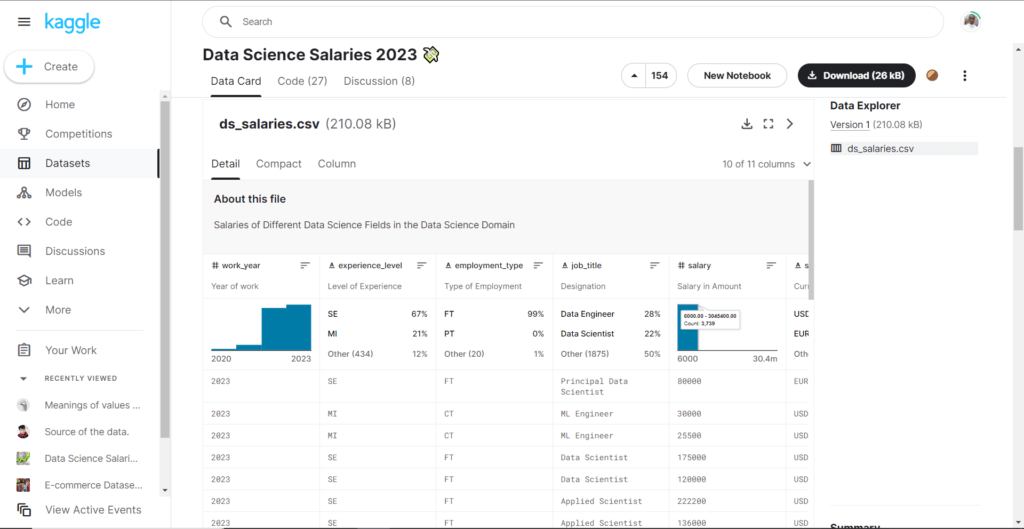
Step 1: Navigate to this Kaggle web page and download the Data Science Salaries 2023 dataset. You can also use other datasets available on Kaggle.
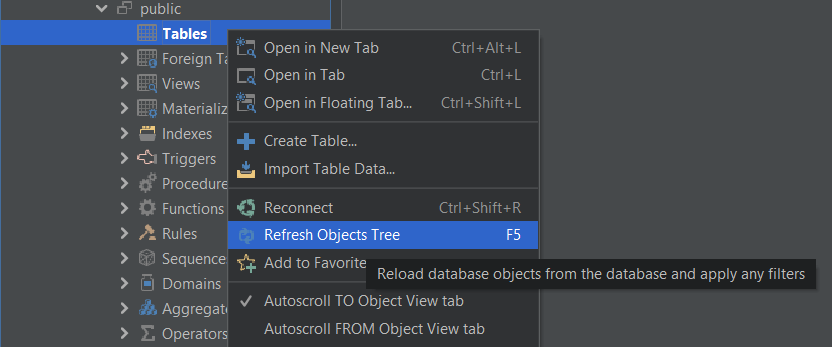
Step 2: Open the database connection PostgresQueryBuilder on DbVisualizer. Right-click the Tables tab tree and select Import Table Data as shown below.

Step 3: Open the Data Science Salaries 2023 CSV file through the window that opens up.

Step 4: Keep clicking the Next button below the popup window until you reach the window below where you need to create a New Database Table.
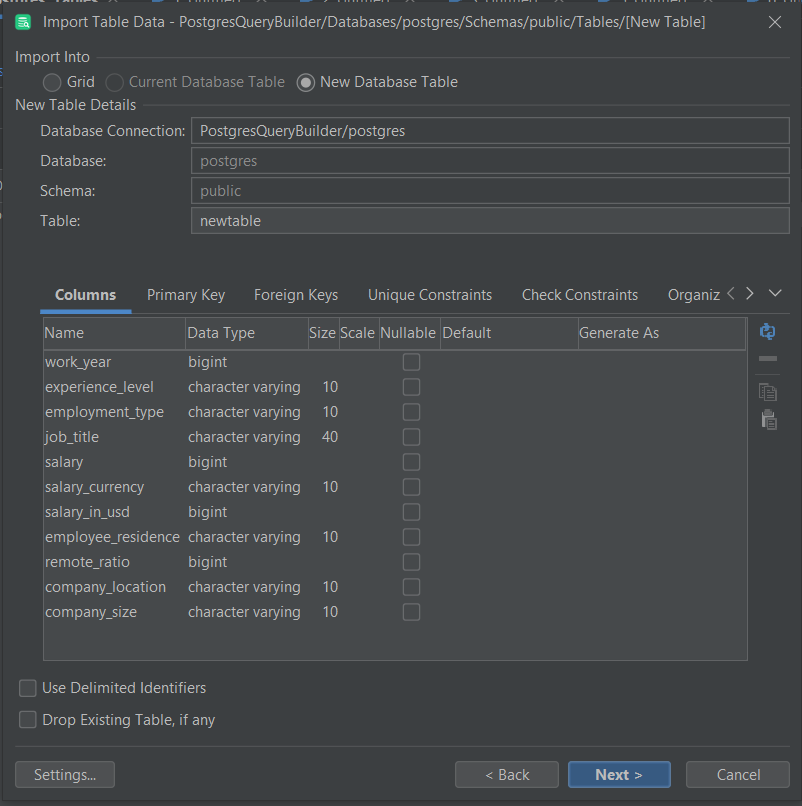
Step 5: In the popup window, give the table that will hold the inventory dataset a name. In this case, I have named my tabledatasciencedataas shown below.
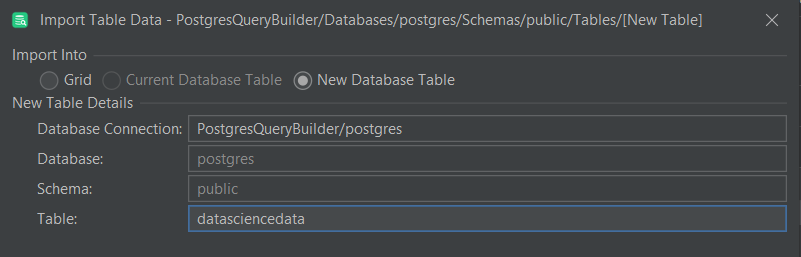
Step 6: Next, check the Use Delimited Identifiers checkbox at the bottom of the pop-up window to help PostgreSQL differentiate any column name from its reserved keywords.

Step 7: Click the Next button and then import the dataset into your PostgreSQL database. If the data is imported successfully, you will get a Success message as shown below.

Once the dataset is imported, right-click on the table tab and refresh to see the table created.
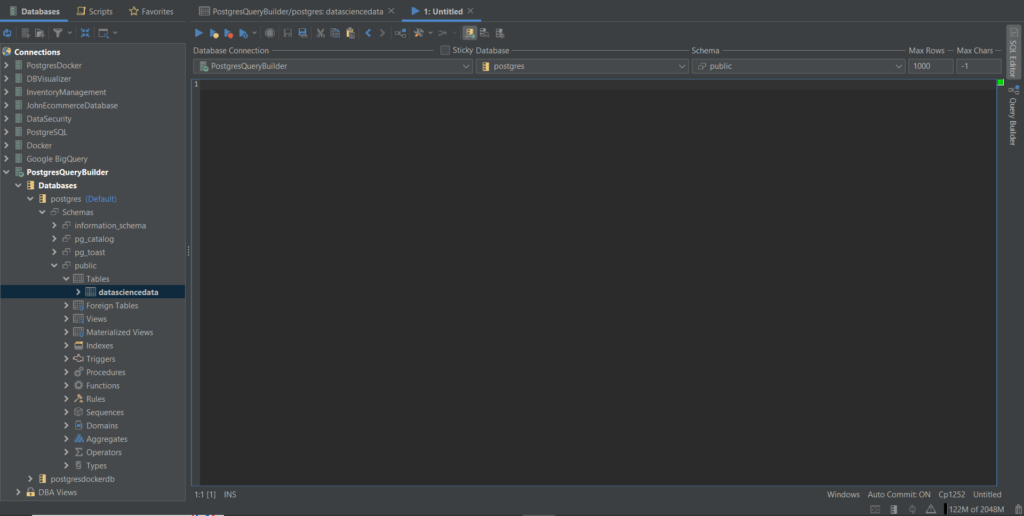
You should be able to see the datasciencedata table created in the Postgres database as shown below.

Generating SQL Queries Using the DbVisualizer Query Builder
The DbVisualizer Query Builder provides an easy way to develop SQL queries by providing a point-and-click interface that does not require in-depth knowledge of the syntax.
Here are the steps to follow to generate SQL queries without coding.
Step 1: Create a new SQL commander tab using (CTRL+T) keys.
Step 2: Open the Query Builder by clicking the vertical Query Builder button on the right.

Step 3: To create a query, drag and drop tables to the Query Builder view.

Step 4: To generate a SQL query, right-click in the column list in the table Window and choose Select All. In this example, we add all columns from the datasciencedata table to the select list:

Step 5: Click the first button above the Query Builder on the left to execute the generated SQL code through the SQL Editor.

You should now see the generated SQL query in the SQL editor – the results of the query should be visible below.
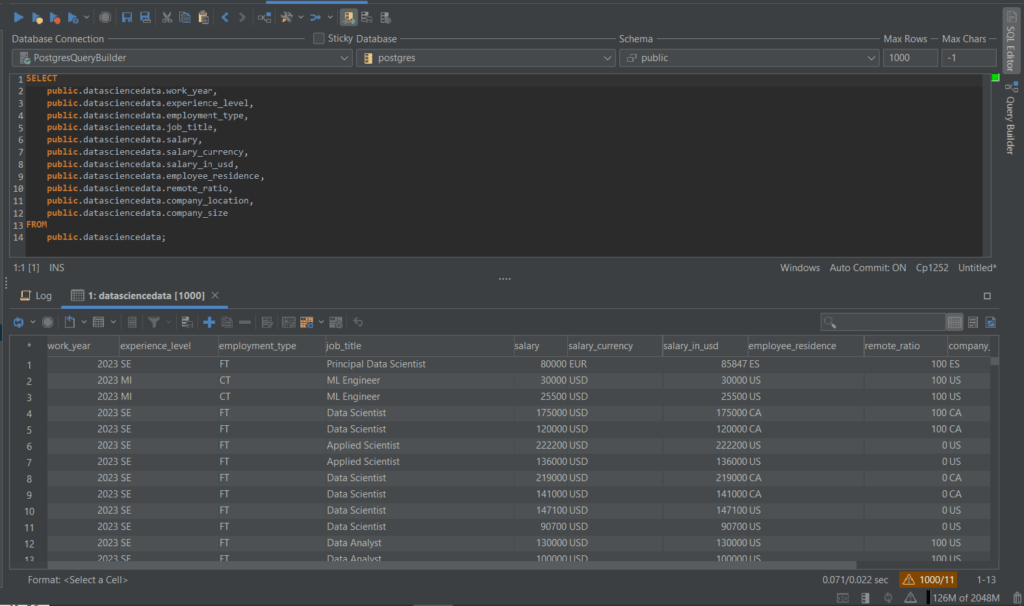
Refining the Query Using The Query Builder
To refine your query, you can use the tabs below the diagram area. When refining the query, keep in mind that we can work with Columns, Conditions, Grouping, and Sorting.
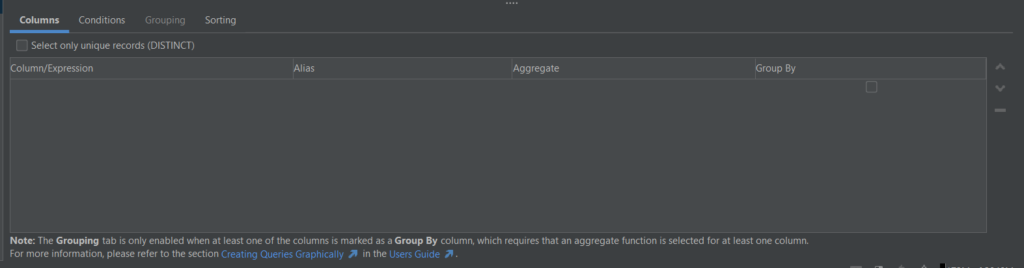
Each of those tabs represents various parts of an SQL query. These parts are explained below:
1
SELECT <Columns>
2
FROM <Tables>
3
WHERE <Conditions>
4
GROUP BY <Columns>
5
HAVING <Grouping>
6
ORDER BY <Sorting>
For example, The Data Science Job Salaries dataset imported into the PostgreSQL database contains eleven columns, which are:
Let’s say you want to generate a SQL query that finds the average salary for each experience level in the dataset. You can do so by using a Query Builder and following the steps below:
Step 1: To find the average salary for each experience level, select the experience_level column on the table added to the Query Builder.

You can now see that the selected column appears under the Columns tab.

You can preview the SQL code generated so far by switching from Edit Details to SQL Preview on the drop-down menu.
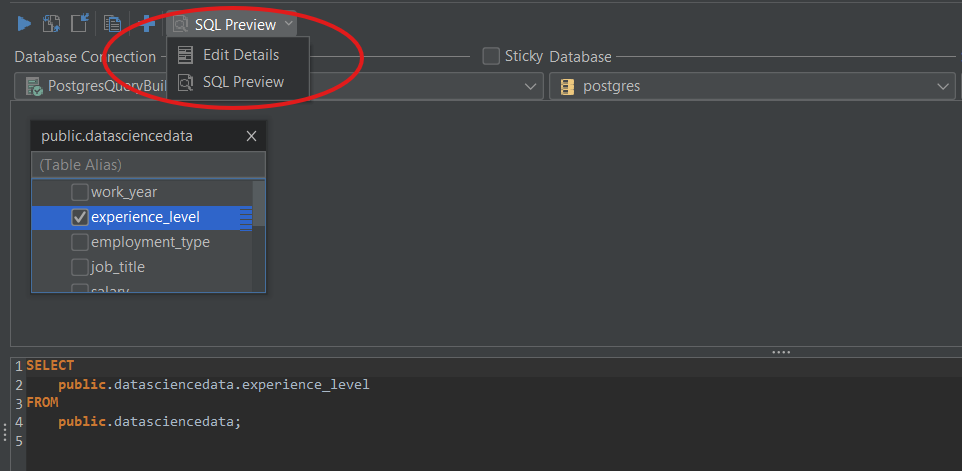
Step 2: Select the salary column from the table on the Query Builder.
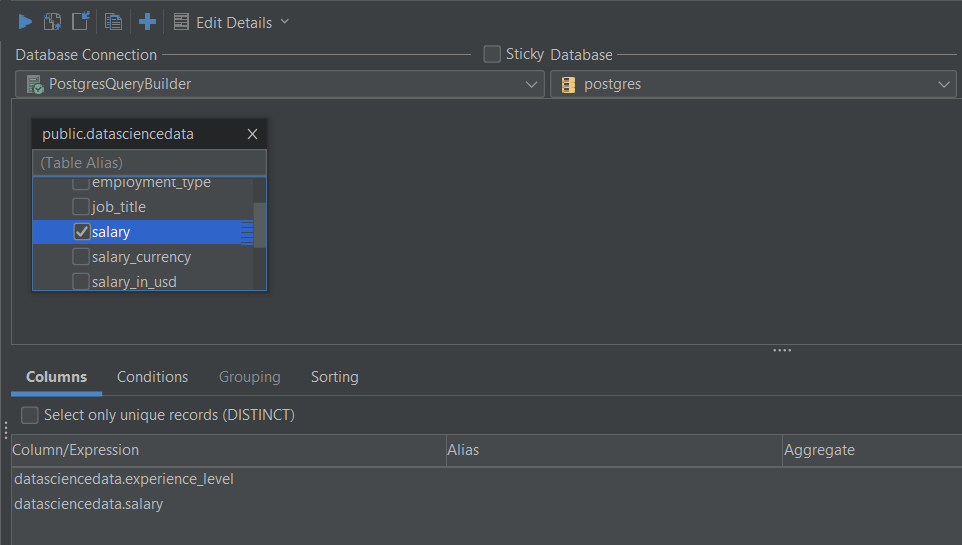
To get the average salary, select the AVG aggregation function under the Aggregate field for the selected salary column.

Let’s give the column that will hold the average salary for each experience level a name. You can call the column average_salary under the Alias field for the salary column.

Step 3: Check the box under the Group By field on the experience_level column to ensure that the average salary is calculated for each unique experience level separately.

Switch from Edit Details to SQL Preview and you will be able to see the SQL query generated by the Query Builder.

Step 4: Click the first button above the Query Builder on the left to copy the generated SQL code to the SQL Editor and execute it. The generated SQL query results in a table with the average salary for each experience level.

That’s it! You’ve now generated a working SQL query all by using features of a powerful SQL client.
Conclusion
Look at this article as a guide on how to generate SQL queries without coding. This article has successfully demonstrated how to build and work with queries using DbVisualizer and provided a couple of examples to generate SQL queries.
If you’ve successfully completed all of the steps outlined in the article, you can now generate SQL queries without much coding knowledge making data analysis operations more accessible and efficient.
Another tool that excels in handling tasks similar to those facilitated by DbVisualizer, especially in generating SQL queries without extensive coding knowledge, is UI Bakery. As a low-code platform for building applications, UI Bakery allows users to seamlessly connect their PostgreSQL databases, enabling them to configure, execute, and integrate SQL queries into their UI components with ease. By offering a user-friendly approach to database querying and app development, UI Bakery makes data analysis operations accessible and efficient, comparable to the capabilities demonstrated by DbVisualizer.
Make sure to try the DbVisualizer SQL client today and until next time.