intro
Let’s learn what happens when deleting a column in SQL and how to do it in the most popular DBMS technologies.
Deleting a column in SQL is one of the most common operations when dealing with a database. For this reason, knowing how to delete a column from a table in SQL is a key skill to have. Without the right procedures and precautions, you could run into data integrity and data loss issues.
In this guide, you will dig into the process of how to delete a column in SQL, exploring the essential concepts and how to do it. At the end of this guide, you will have all the information required to perform column deletion operations smoothly and effectively.
Let’s dive in!
What Does It Mean to Delete a Column in SQL?
Deleting a column in SQL refers to the process of permanently removing a specific column from a table. All data associated with the column will be removed from the disk. Similarly, the column’s metadata will be removed from the table's schema.
When you delete a column, you essentially eliminate its existence within the table structure. The column will be no longer available for queries and its data will be lost.
Consequences of Deleting a Column in SQL
Here are the key aspects to consider when removing a column from a table in SQL:
Keep in mind that deleting a column is an operation that cannot be undone. This means that you must be careful with it, especially in production environments. Before proceeding with the irreversible operation, it is essential to plan properly, back up the database, and consider the potential impact on existing applications and queries.
For further reading on how to perform and and deal with backups in databases, check out our guides:
Syntax to Delete a Column in SQL
The SQL command to delete an existing column from a table is DROP COLUMN, with is part of the SQL DDL. That stands for “Data Definition Language” and contains statements to define, modify, or delete the structure of database objects like tables, indexes, and constraints.
Since DROP COLUMN involves modifying the structure of an existing table, it must be used in an ALTER TABLE query.
Here is the generic SQL syntax to delete a column from a table:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name DROP COLUMN column_name;
Where:
For more information, refer to our specific guide on how to the ALTER TABLE DROP COLUMN statement.
Later in this article, you will see how to use this query in the most popular relational databases, such as MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and Oracle.
How to Delete a Column From a Table in SQL
In this section, you will see how to delete one or more columns in the most popular relational databases:
Time to see how to delete a column in SQL technologies!
Deleting a Column in MySQL
The syntax to delete a single column in MySQL is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP [COLUMN] column_name;
Note that the COLUMN keyword is optional. For more details about this query, read our article on the MySQL ALTER TABLE statement.
For example, you can remove the email column from the users table with:
1
ALTER TABLE users
2
DROP COLUMN email;
The syntax to delete multiple columns with a single query in MySQL is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP [COLUMN] column1,
3
DROP [COLUMN] column2,
4
...,
5
DROP [COLUMN] columnN;
Again, COLUMN is optional.
So, the query to remove the phone and address columns from the contacts table is:
1
ALTER TABLE contacts
2
DROP phone,
3
DROP address;
Deleting a Column in PostgreSQL
The syntax to delete a single column in PostgreSQL is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP [COLUMN] column_name;
The COLUMN keyword is optional.
For example, you can remove the address column from the users table with:
1
ALTER TABLE users
2
DROP COLUMN address;
Instead, the syntax to delete more than one column with a single PostgreSQL query is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP [COLUMN] column1,
3
DROP [COLUMN] column2,
4
...,
5
DROP [COLUMN] columnN;
Again, COLUMN is optional.
Thus, below is the query to delete the price and quantity columns from the orders table:
1
ALTER TABLE orders
2
DROP COLUMN price,
3
DROP COLUMN quantity;
Deleting a Column in SQL Server
The syntax to delete a single column in SQL Server is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP COLUMN column_name;
For instance, you can drop the release_date column from the games table with:
1
ALTER TABLE games
2
DROP COLUMN release_date;
To delete multiple columns with a single T-SQL query is, the syntax is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP COLUMN column1, column2, ..., columnN;
Note: The above syntax is different from that of MySQL and PostgreSQL.
Therefore, this is the query to remove the time and efforts columns from the projects table:
1
ALTER TABLE projects
2
DROP COLUMN time, effort;
Deleting a Column in Oracle
The syntax for deleting a column in SQL using Oracle is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP COLUMN column_name;
For example, you can remove the price column from the products table with:
1
ALTER TABLE products DROP COLUMN price;
Instead, the syntax to delete multiple columns at the same time is:
1
ALTER TABLE table_name
2
DROP (column1, column2, ..., columnN);
Note how COLUMN disappears from the ALTER TABLE ... DROP COLUMN query for a single query. Also, you must list the columns to delete, separated by commas, between parentheses
Then, the following query deletes the address and age from the users table:
1
ALTER TABLE projects
2
DROP (address, age);
Note that Oracle also allows you to logically delete a column with the SET UNUSED command.
Visually Remove a Column in SQL: Complete Example
When deleting a column in SQL, you must follow the appropriate procedure. You cannot simply execute a DROP COLUMN statement without careful consideration, as it will permanently remove data from your table.
Ideally, you should be able to see the impact of your query visually to understand how it affects your database schema. This is where a database client like DbVisualizer becomes invaluable!
DbVisualizer allows you to visually explore your tables and data, making it easier to monitor your database and address issues as they arise. This visual insight helps ensure that changes are made thoughtfully and with full awareness of their consequences.
Also, DbVisualizer lets you delete a column visually, without needing to manually execute a query. Let’s see how!
Step #1: Reach and Explore Your Table
Download DbVisualizer for free and follow the wizard to set up a database connection.
Suppose you have a companyMySQL database. Navigate to the users table and open the “Columns” dropdown. Right-click on “Columns” and select the “Open in New Tab” option:

Here, you can visually explore all the columns your employees table consists of.
Step #2: Visually Altering the Table
Right click on the employees table and select the “Alter Table...” option:

This will open the following modal:
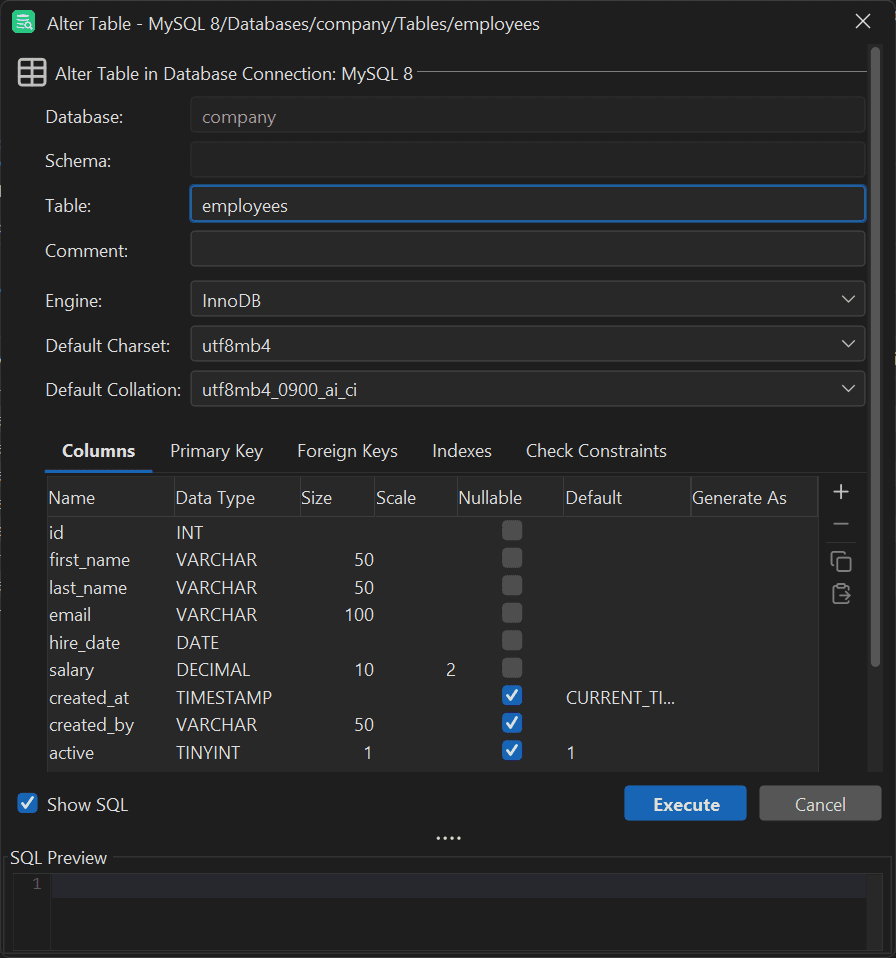
Here, select the active column, click the “-” button, and then run the “Execute” button:

Under the hood, DbVisualizer will run the following query you can see in the “SQL Preview” section:
1
ALTER TABLE
2
`company`.`employees` DROP COLUMN `active`
In other words, it performs the correct DROP COLUMN statement for you. Equivalently, you can open the SQL Commander and launch manually launch the query:

In both cases, the is_active column will be removed from employees.
Step #3: Verify Column Removal
To make sure that the column was removed, right-click on “Columns” and select the “Refresh Objects Tree” option:

This will refresh the column list, and you should notice that is_active is now gone:

Et voilà! You just deleted a column visually with just a few simple clicks!
Best Practices When You Delete a Column in SQL
Best practices help prevent data loss and minimize disruptions when deleting a column in SQL, especially in a production environment. Some considerations to keep in mind before proceeding are:
Conclusion
In this article, you saw what it means to delete a column in SQL, what happens when you do it, and how to do it. Thanks to what you learned here, you now know how to handle single and multiple column deletion in MySQL, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Oracle Database.
Since deleting columns in SQL alters schema of your database, monitoring the consequences in a database client makes everything easier. This is where DbVisualizer comes in!
In addition to supporting visual querying, column management, and data exploration in dozens of databases, DbVisualizer also offers advanced query optimization capabilities, and ER-like schema generation. Download DbVisualizer for free now!
FAQ
What is the difference between dropping a column and deleting a column in SQL?
In SQL, dropping a column and deleting a column mean the same things. The two expressions refer to the process of permanently removing a column from a table, including its data and metadata.
How to delete a value from a column in SQL?
To "delete a value from a column" in SQL means setting it to NULL, assuming the column is nullable. You can achieve that using the UPDATE statement below:
1
UPDATE table_name
2
SET column_name = NULL
3
WHERE condition;
If the column does not allow NULL, you would need to set it to a default or alternative value. Discover more in our blog post on working with NULL.
What is the difference between deleting a column logically and deleting a column physically?
The distinction between logical and physical deletion in a relational database lies in how data removal is applied. Logical deletion involves marking the data as inactive without physically removing the column. On the other hand, physical deletion involves permanently removing the data from the database, making it unrecoverable.
Is it possible to delete multiple columns in a single SQL statement?
In most SQL dialects, you can remove more than one column with a single ALTER TABLE query by using a special syntax. In such a scenario, you have to specify all the columns you want to delete in a list or use the DROP COLUMN command several times.
What happens when you try to delete a column that does not exist?
When attempting to delete a column that does not exist in the table, the database will raise an error. For example, MySQL returns the following error message:
1
Can't DROP 'column_name'; check that column/key exists
Thus, ensure that the columns you want to delete exist in the table before launching the command.
How to delete a column in a foreign key constraint?
To delete a column that is part of a foreign key constraint, you must first drop the constraint:
1
ALTER TABLE child_table DROP CONSTRAINT fk_constraint_name;
Once the foreign key is removed, you can safely delete the column:
1
ALTER TABLE child_table DROP COLUMN column_name;
Before launching the SQL query to delete a column from a table, check that the column is not referenced elsewhere (e.g., indexes, constraints).