intro
Let’s learn everything you need to know about the SQL Server SUBSTRING function to extract a portion of a specified character, binary, text, or image expression.
If you have ever written code or worked with strings, you know how common it is to extract substrings. It is such a frequent task that SQL Server includes a built-in function specifically for it. In particular, the SQL Server SUBSTRING function lets you extract specific portions of data from a string.
In this guide, you will learn what the SUBSTRING SQL Server function is, how it works, and how to use it through practical examples.
Let’s dive in!
What Is SUBSTRING in SQL Server?
In SQL Server, SUBSTRING is a built-in function that extracts a portion of a character, binary, text, or image expression. As you can see, the SQL Server SUBSTRING function works with different data types, making it a versatile tool for string manipulation.
This function is commonly used to extract specific parts of a string, especially when those parts have a fixed length. For example, it can be useful for extracting the date portion from a standard timestamp stored as a text string.
SQL Server SUBSTRING: Syntax and Notes
This is the syntax of SUBSTRING in SQL Server:
1
SUBSTRING ( expression , start , length )
Where:
The return type is:
For example, this is how you can use the SUBSTRING function in SQL Server to extract “Hello” from “Hello, World”:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING('Hello, World', 1, 5);
The result will be:
1
'Hello'
The result is “Hello” as that string goes from index 1 (“H”) to 5 (“o”) using a 1-based index.
Notes:
SUBSTRING SQL Server Examples
Now that you know what the SUBSTRING SQL Server function is, you are ready to explore some real-world examples.
Note: The examples below are executed in SQL Server database client DbVisualizer, a top-rated database client. However, any other database client can also be used.
Time to see SQL Server SUBSTRING in action!
Use SUBSTRING on String Data for Programmatic Substring Extraction
Imagine you have a Users table containing user data, including email addresses:

Exploring the data in the Users table in DbVisualizer
Your goal is to retrieve the domain name from each email. This is how you can achieve that with SUBSTRING:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING(Email, CHARINDEX('@', Email) + 1, LEN(Email)) AS Domain
2
FROM Users;
The CHARINDEX function finds the position of the @ symbol, and SUBSTRING starts from the character after @ and extracts the rest of the email as the domain.
The result will be as follows:
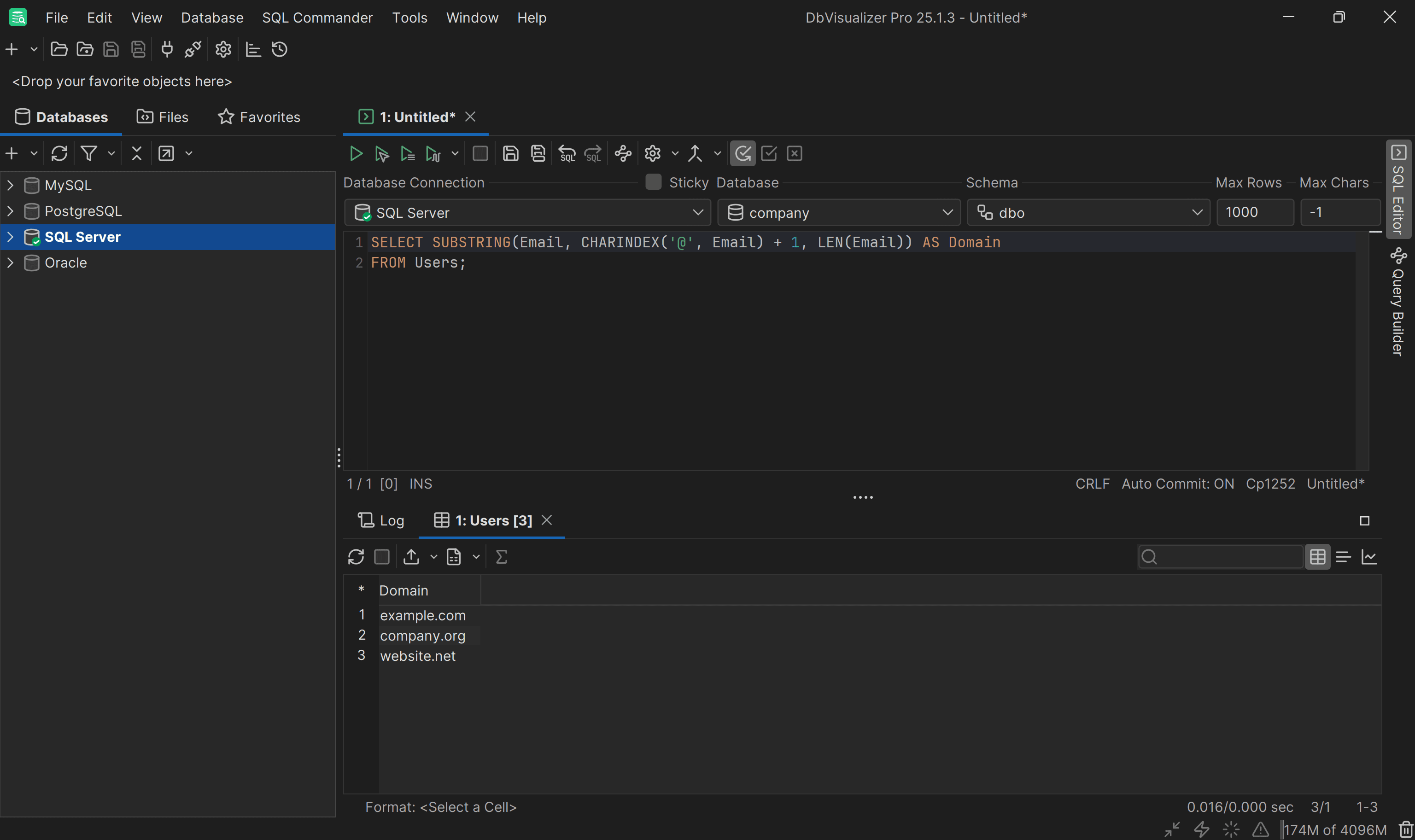
As you can see, the query managed to extract the email address domains as desired.
Use SUBSTRING with Datetimes
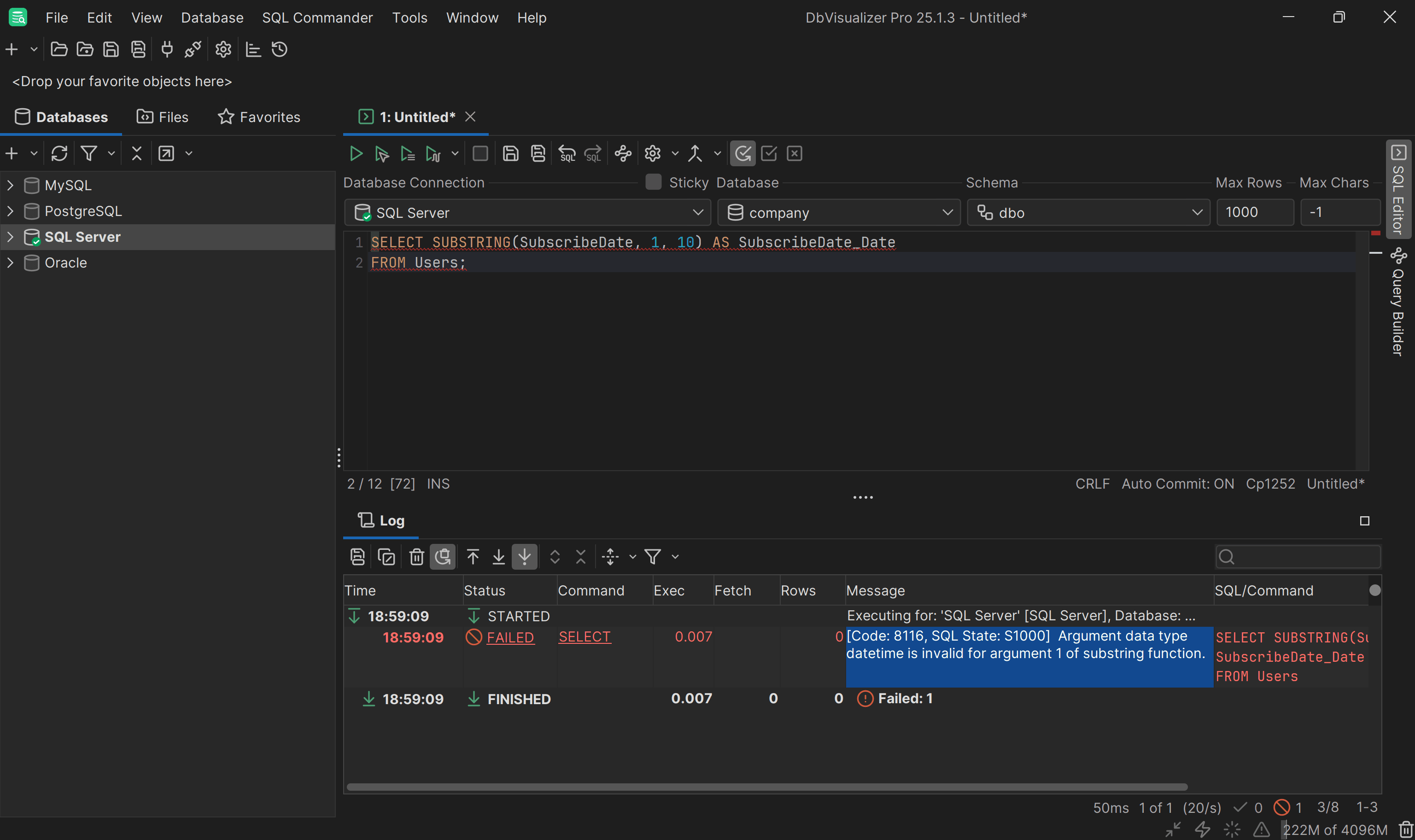
In the Users table, the SubscribeDate column is a datetime value that stores the exact date and time a user subscribed. If you want to extract just the date portion (the first 1 character), you might be tempted to write:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING(SubscribeDate, 1, 10) AS SubscribeDate_Date
2
FROM Users;
However, this will result in an error because SubscribeDate is a datetime, not a string:
1
Argument data type datetime is invalid for argument 1 of substring function.
To fix that error, you need to cast the datetime data to a string first with the
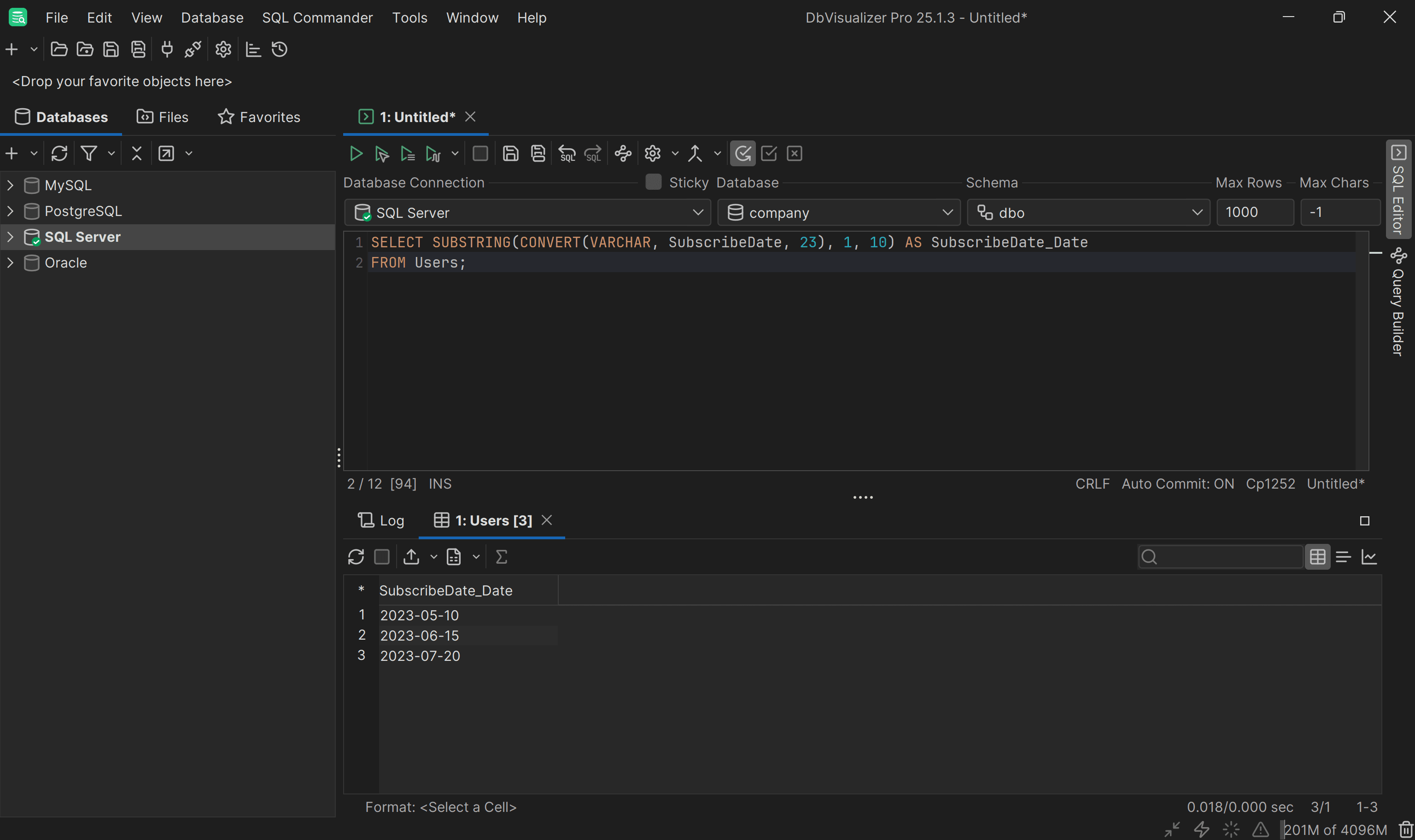
This time, the query will work as expected and return only the date. Learn more in our guide on extracting time and date in MS SQL Server.
Use SUBSTRING on Binary Data
The SQL Server SUBSTRING function also works with binary data, as in this example:
1
SELECT SUBSTRING(0x48656C6C6F20576F726C64, 1, 5) AS Result;
0x48656C6C6F20576F726C64 is the binary representation of the “Hello, World” string. So, the result will be “Hello” in binary format, as you can verify in the special data binary viewer in DbVisualizer:

Note that the result is in binary data as the input is in binary data.
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned about the SQL Server SUBSTRING function, including how it works, its syntax, and when to use it. As shown, DbVisualizer makes working with these functions easier thanks to its full support for SQL Server, detailed error messages, and visual representation of both binary and text data. Other helpful features include SQL formatting, ERD-style schema diagrams, and tools for query optimization. Download DbVisualizer for free today!
FAQ
Does the SQL Server SUBSTRING function also work on non-text data?
Yes, in addition to text types, the SUBSTRING function in SQL Server works on non-text data types like binary, varbinary, and image. It extracts a portion of the value based on the specified starting position and length.
What other databases support the SUBSTRING function?
The SUBSTRING function is supported by many popular databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, Oracle, and SQLite. Keep in mind that the syntax may vary slightly, but the core functionality remains the same. Note that some databases also support the alias SUBSTR. For example, learn more in our guide on the MySQL SUBSTRING function.
Can you use SUBSTR in SQL Server?
No, SUBSTR is not available in SQL Server as an alias for SUBSTRING as it occurs in other databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL.
What is the alternative to SUBSTRING_INDEX SQL Server function?
SQL Server does not have a built-in SUBSTRING_INDEX function like MySQL. However, you can achieve similar results using a combination of CHARINDEX, SUBSTRING, and sometimes PARSENAME or STRING_SPLIT, depending on your use case. These functions help extract parts of a string based on a delimiter.
What are some useful string manipulation functions in SQL Server?
Here are some other useful string manipulation functions in SQL Server:
Why use a visual database client?
A visual database client like DbVisualizer simplifies working with databases and managing data, including text and binary data. It provides an intuitive interface for managing tables, exploring schema relationships, and writing/debugging queries with a powerful SQL editor. Specifically, features like autocomplete, ER diagrams, and data export tools set DbVisualizer apart from its competitors. Try the Pro version with a 21-day free trial!