intro
Learn how to use COALESCE in SQL through some real-world examples in different RDBMS technologies.
NULLs are tricky, and databases have found different ways to deal with them. This is such a common problem that the SQL standard involves functions to handle them consistently. In most cases, you need to replace NULLs with default values, which is what the SQL COALESCE function is all about!
In this article, you will discover everything you need to know about COALESCE, exploring its syntax, how it works, the DBMSs that support it, and its use cases.
Let's dive in!
What Is COALESCE in SQL?
COALESCE is an SQL function that accepts a list of parameters and returns the first non-NULL value from the list. Here is what the syntax looks like:
COALESCE(expression1, expression2, expression, ...) expression1, expression2, expression3, and so on, are the parameters (values or expressions) to be evaluated.
Usually, the SQL COALESCE function is used for NULL handling in the database. Instead of replacing NULL values at the application level, it allows you to deal with them directly at the data retrieval time.
How To Use the COALESCE SQL Function
To understand how to use COALESCE in SQL, you first need to learn how it works:
- The function evaluates the expressions received as input from left to right.
- It returns the first non-
NULLexpression it encounters. - If all expressions are
NULL, it returnsNULL.
In other words, to use the COALESCE SQL function, you have to specify your columns, expressions, or values so that if an element is NULL, it will be replaced by the element to its right, and so on. To better understand how this mechanism works, consider this sample query:
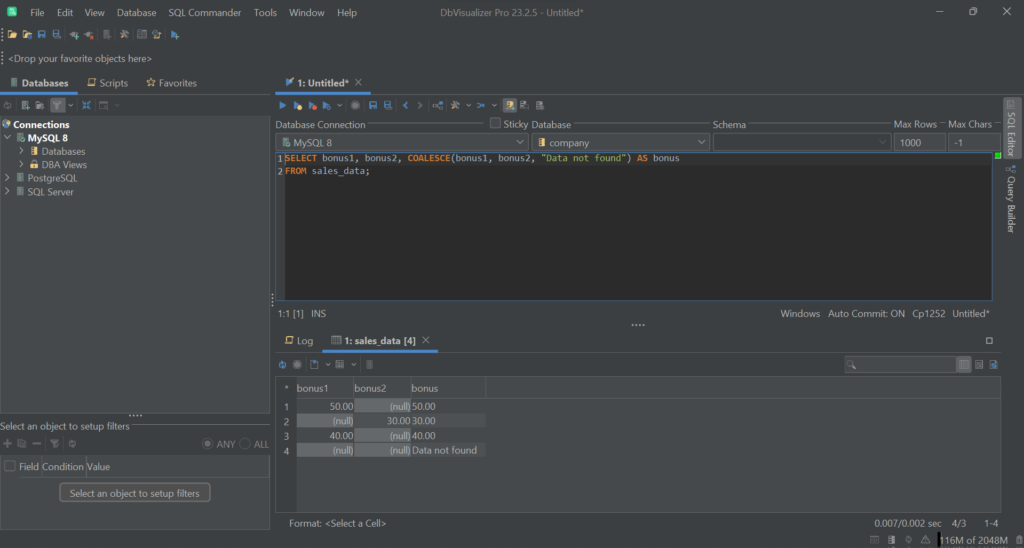
1
SELECT COALESCE(bonus1, bonus2, bonus3) AS bonus
2
FROM sales_data;
As you can verify from the image below, it returns:
- “Data not found” when bonus1 and bonus2 are NULL.
- bonus1 when bonus1 is not NULL.
- bonus2 when bonus1 is NULL and bonus2 is not NULL.
Databases That Support COALESCE
COALESCE has been part of the ANSI SQL standard since 1992 and it is also an SQL reserved keyword. This means it is not a new feature and most RDBMS technologies provide a standard-compliant implementation.
The list of databases that support the SQL COALESCE function include:
- MySQL
- PostgreSQL
- SQL Server (T-SQL)
- Oracle Database
- SQLite
- IBM Db2
- MariaDB
- Amazon Redshift
- Google BigQuery
- Snowflake
All these DBMSs provide a COALESCE function that respects the syntax and logic presented earlier. The function is so widespread that finding modern database technologies that do not offer it is not easy. However, some proprietary or older database systems may not support it. This is generally not a problem as you can achieve the same result with custom logic or a CASE statement.
Check out our guide for an in-depth tutorial on PostgreSQL COALESCE.
SQL COALESCE Function: Use Cases
Now that you know how to use COALESCE in SQL, it is time to explore some popular use cases.
Note: The examples below are in MySQL, but the following scenarios apply to any DBMS that supports COALESCE. The query will be run in DbVisualizer, a fully-featured database client that supports dozens of databases.
Providing Default Values
The most common COALESCE SQL example involves using the function to provide default values for columns or values that might be NULL.
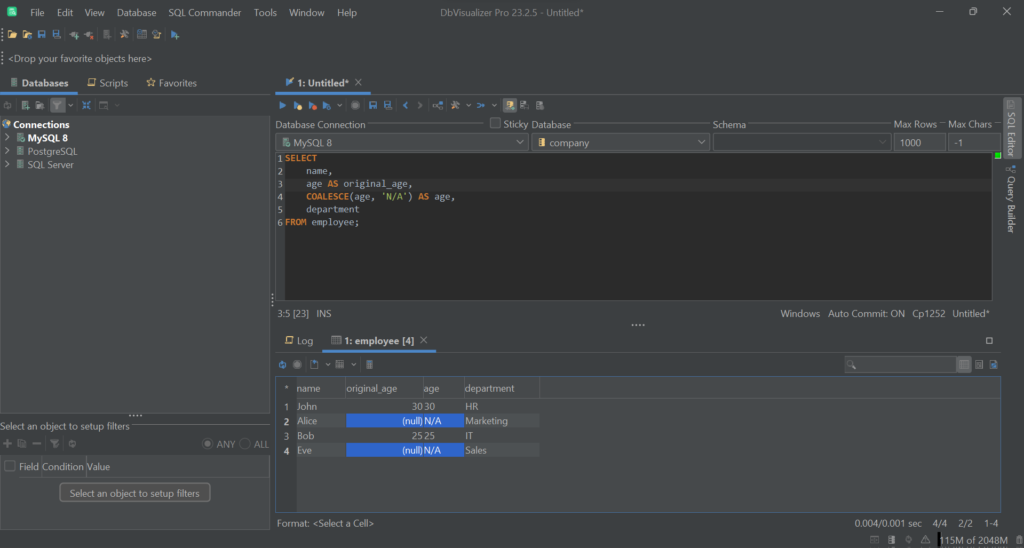
For example, suppose you want to display the string "N/A" for missing data in a report. You can get this result directly in the database with the following query:
1
SELECT
2
name,
3
COALESCE(age, 'N/A') AS age,
4
department
5
FROM employee;
Handling NULL Values in Math Operations
Databases can produce unexpected behavior when adding, dividing, or multiplying by NULL values. To avoid that, you can use the SQL COALESCE function to replace the NULLs with more consistent values.
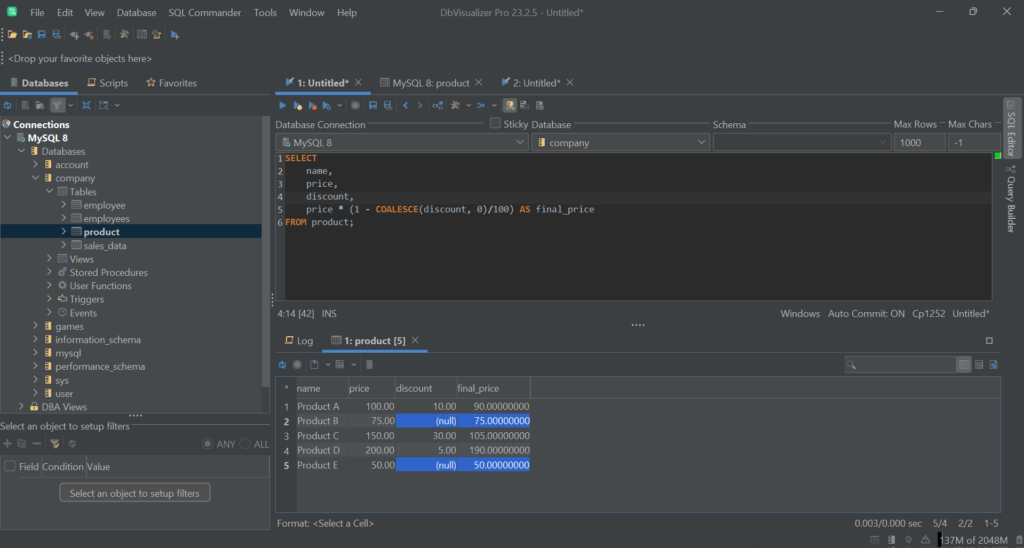
Consider for example the query below:
1
SELECT
2
name,
3
price,
4
discount,
5
price * (1 - COALESCE(discount, 0)/100) AS final_price
6
FROM product;
As you can notice in the following image, COALESCE makes sure that it produces consistent results even when discount is NULL.
Similarly, you can use this mechanism when using SQL aggregate functions:
1
SELECT
2
category,
3
SUM(COALESCE(price, 0)) as global_price
4
FROM product
5
GROUP BY category;
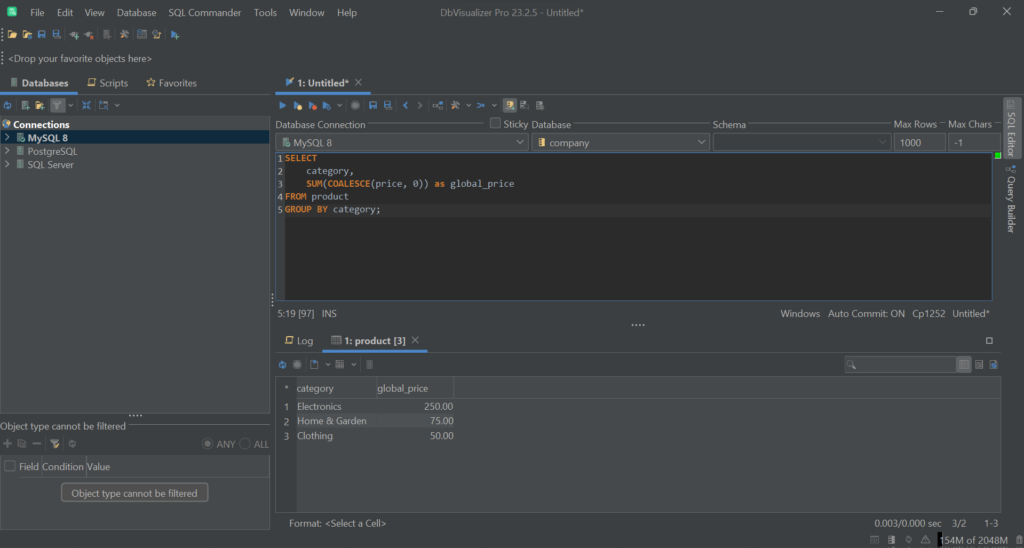
Sorting and Ordering
COALESCE can be used to control the sorting order of result sets, ensuring that NULL values are treated as expected.
1
SELECT name, COALESCE(priority, 0) AS priority
2
FROM tasks
3
ORDER BY priority;

DBMS technologies behave differently when it comes to ordering values that may be NULL, but this approach leads to consistent and predictable results.
Without COALESCE, you would get a different sorting:

Note that “Task 2” and “Task 4” moved from the bottom to the top of the resulting table.
Et voilà! You just became a COALESCE SQL master!
Conclusion
In this guide, you learned what the SQL COALESCE function is and how it works. You now know that it is a powerful, standards-compliant, and easy-to-use function for handling NULL values directly in the database.
To better appreciate its capabilities, you need a tool that allows you to visually explore query results. This is where a comprehensive database client like DbVisualizer comes in! In addition to supporting several DBMSs, this tool offers advanced query optimization capabilities, ERD-like schema generation, and much more. Try DbVisualizer for free today!
FAQ
What does COALESCE do in SQL?
The COALESCE SQL function accepts a comma-separated list of arguments and returns the first argument that is not NULL.
How is COALESCE implemented in SQL?
COALESCE is implemented just like in the syntax below:
COALESCE(expression1, expression2, expression3, ...)
As such, COALESCE is nothing more than a shorthand for the following SQL CASE expression:
1
CASE WHEN expression1 IS NOT NULL THEN expression1
2
WHEN expression2 IS NOT NULL THEN expression2
3
WHEN expression3 IS NOT NULL THEN expression3
4
...
5
END
What is the difference between COALESCE vs ISNULL?
COALESCE is a standard SQL function supported by most databases. Its purpose is to handle multiple values and provide the first non-NULL result. In contrast, ISNULL is not a standard function and behaves differently in different databases. For example, on SQL Server, it returns a specified value if the expression is NULL. So, the COALESCE vs ISNULL comparison depends on the DBMS.
Is the SQL COALESCE function part of ANSI SQL?
The COALESCE SQL function was introduced to the SQL ANSI standard in SQL-92 (also known as SQL2). SQL-92 is a widely adopted SQL standard that was published in 1992. This is why it is supported by most relational database management systems and has become a common feature in SQL databases.
Does Microsoft Access support the COALESCE SQL function?
Microsoft Access does not support the COALESCE function. Instead, you can use the native IIf or Nz functions to handle NULL values and achieve similar functionality.