intro
JSON is one of the most popular human-readable data formats. PostgreSQL allows you to store JSON data and perform queries on it thanks to the json and jsonb data types. The introduction of these JSON data types represented a game-changing moment for relational databases and opened up many new opportunities.
Now, you may be wondering why PostgreSQL has two JSON data types, what the main differences between them are, and when you should use json vs jsonb and vice versa. Keep reading and by the end of the article, you will be able to answer all these doubts!
In this PostgreSQL json vs jsonb guide, you will learn:
Let’s dive in!
JSON Data Type
PostgreSQL introduced the json data type with Postgres 9.2. This represented a turning point because it allowed Postgres to start becoming a direct competitor to NoSQL technologies.
At the same time, the introduction of the json data type was not a revolution...
The reason is that the PostgreSQL json data type is not much more than a simple text field. Read our article to learn the difference between the Postgres text vs varchar data types.
In particular, the json data type does not offer many useful features. You can perform some basic JSON operations, such as extracting the value associated with an object key. However, these operations are rather slow and are not optimized for large JSON data.
Note that json stores JSON data in a raw format. This means that Postgres preserves the original key orders, whitespace, and even duplicate keys in objects. Also, Postgres enforces that the data stored in these fields is valid JSON.
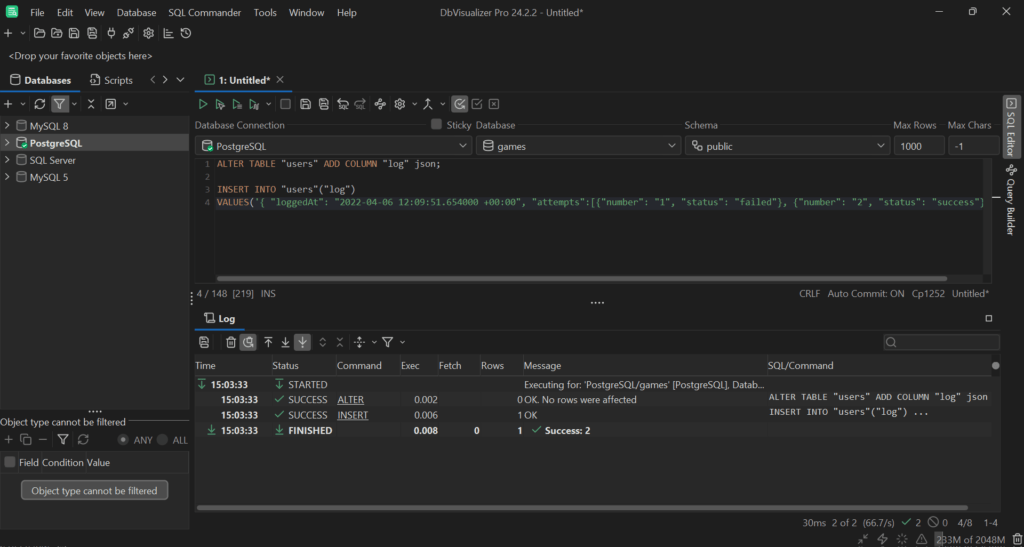
You can add a json column to a table with the following ALTER TABLE query:
1
ALTER TABLE "users" ADD COLUMN "log" json;
Then, you can insert data in the log column as in the example below:
1
INSERT INTO "users"("log")VALUES('{ "loggedAt": "2022-04-06 12:09:51.654000 +00:00", "attempts":[{"number": "1", "status": "failed"}, {"number": "2", "status": "success"}] }');
This is pretty much everything you can do with json.
Time to explore the PostgreSQL jsonb data type!
JSONB Data Type
PostgreSQL added the jsonb data type in Postgres 9.4, which is when the JSON support in PostgreSQL became real. Note that the 'b' at the end of the data type name stands for 'better'. That is because jsonb stores JSON data in a special binary representation, whose format is compressed and more efficient than text. For all information, read our guide on jsonb.
In detail, jsonb is based on an optimized format that supports many new operations. For example, extracting the value associated with an object key becomes lightning fast. Also, jsonb allows you to:
You can take a look at all the built-in jsonb functions offered by PostgreSQL in the official documentation. Additionally, check out our guide on PostgreSQL JSONPATH.
On top of those operations, jsonb also supports an existence operator. This gives you teh ability to test whether a string appears as an object key or array element. You can use it as follows:
1
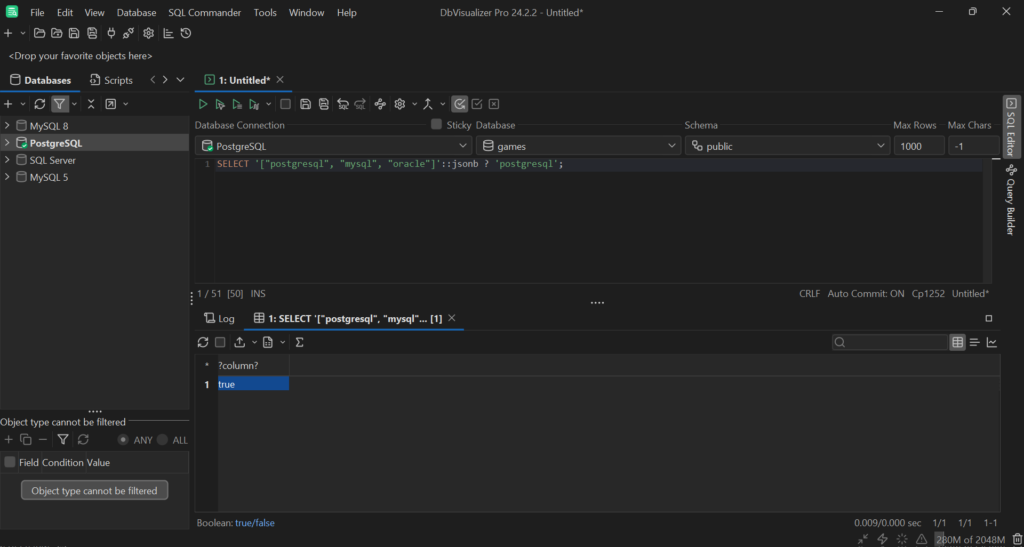
SELECT'["postgresql", "mysql", "oracle"]'::jsonb ? 'postgresql';
The above query verifies if the JSON array includes the 'postgresql' string element. Run the query, and you will get a true result:
Plus, jsonb supports GIN (Generalized Inverted Index) indexes. These provide the ability to efficiently search for keys and/or key/value pairs in a large number of jsonb documents.
You can add a jsonb column to an existing table with the ALTER TABLE statement below:
1
ALTER TABLE "users" ADD COLUMN "config" jsonb;
Then, you can insert data in such a column as below:
1
INSERT INTO "users"("config")
2
VALUES('{"subscriptionLevel": "hero", "points": 450, "achievements": [4, 7, 9], "skins": {"special": true, "hallowing": true, "christmas": false}}');

Wonderful, now that you know what these two data types for dealing with JSON data are, you are ready to delve into the Postgres jsonvs jsonb comparison!
What Do JSON and JSONB Have in Common?
As stated in the official PostgreSQL documentation, the json and jsonb data types basically accept the same sets of values as input. Conceptually, this is the main aspect the two data types share.
Apart from that, they do not have many other things in common. Specifically, you can see jsonb as a kind of successor to json. Although there are specific cases where json is better than jsonb, as you are about to learn.
JSON vs JSONB: Main differences
The main difference between json and jsonb lies in the way they store data behind the scenes. Specifically, the json data type stores an exact copy of the input text. Thus, each function and operation has to reparse the entire field at each execution. Instead, jsonb relies on a more efficient format, which makes it inherently faster than json.
Still, the different behavior of json can also represent an advantage over jsonb. This is because json preserves the indentation of the input data. So, if you need to be careful about JSON formatting, the json PostgreSQL data type can be useful.
Instead, jsonb stores data in a decomposed binary format. This makes INSERT statements a bit slower compared to json due to conversion overhead. However, the jsonb binary format is significantly faster to process as it does not involve reparsing. Also, jsonb supports many more functions and operators than json.
Moreover, jsonb supports indexing, which can lead to significant performance advantages when parsing and querying JSON data.
What to Choose Between JSON and JSONB
Let's try to understand when you should prefer json over jsonb and vice versa with some real-world scenarios. This is the last step of this PostgreSQL json vs jsonb comparison!
JSON
The json data type works better than jsonb when:
Basically, json is perfect for storing logs. This is especially true if you already know that your log data comes in valid JSON format. For that scenario, text is also a viable option.
JSONB
In PostgreSQL, the jsonb data type is better than its counterpart in pretty much every other situation. Some examples of where you could adopt jsonb include:
In general, you should use jsonb whenever you have to deal with dynamic JSON data or when you need to perform advanced queries.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL supports JSON data through the json vs jsonb data types. In most scenarios, jsonb is the perfect solution if you are looking for a NoSQL-like data type. On the other hand, there are some specific situations where json can have its place. Here, you learn what json and jsonb are, how they work, and when to adopt one or the other.
Keep in mind that DbVisualizer, the popular and feature-rich database client, fully supports all PostgreSQL data types. DbVisualizer is a top-rated PostgreSQL client that comes with advanced features like query optimization and ERD-like schema export. Download DbVisualizer for free!
Thanks for reading! We hope that you found this article helpful.
FAQ
What are the main elements to keep in mind in the json vs jsonb Postgres comparison?
Storage Format:
Performance:
Flexibility:
Indexing:
Which is better between jsonb vs json?
jsonb is generally better than json in PostgreSQL for most use cases. It stores data in a binary format, making it faster and more efficient for querying, indexing, and operations. jsonb also supports indexing, which improves performance for search and retrieval tasks. However, json might be preferable if you need to preserve the exact text formatting of the JSON data, as jsonb may reorder keys and remove whitespace.
Which wins the PostgreSQL json vs jsonb performance race?
jsonb wins the performance race as it stores JSON data in a binary format, making it more efficient for querying compared to json, which stores data as plain text. Plus, jsonb supports indexing on JSON fields, leading to faster search and retrieval, while json requires re-parsing the text for operations, resulting in slower performance.