intro
A PostgreSQL server can have several users, and there are different ways to list them all. Explore three different approaches to list users in Postgres.
Keeping track of users is a common task that database administrators must frequently perform. For PostgreSQL, there are a couple of Postgres list users procedures available, and the best one depends on your experience and the specific use case.
In this article, you will explore two different approaches to getting the list of users in PostgreSQL:
Let’s learn how to list users in Postgres!
List All Users in Postgres With psql
psql stands for "PostgreSQL interactive terminal” and is a tool for interacting with a PostgreSQL server via the command line. In detail, it allows you to:
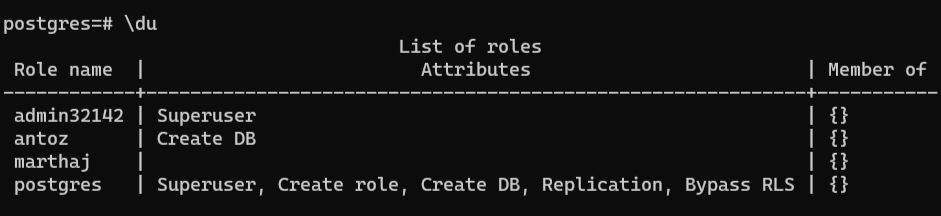
Now that you know what psql is, follow the steps below to run the Postgres list users \du command:
psql -U <username>
Replace <username> with the username of the PostgreSQL user you want to log in with. For example, replace it with the “postgres” username. After that, psql will ask you to enter the user's password. Type in it and press Enter to log into the server.
\du
This command will produce a table containing the users in the PostgreSQL server:
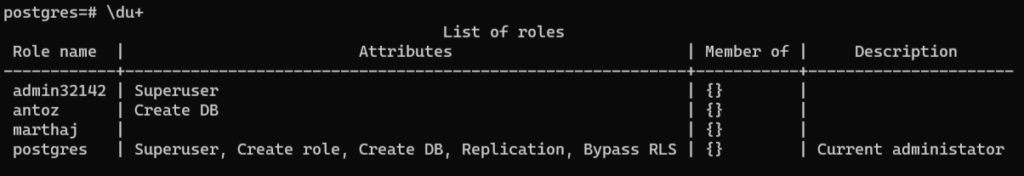
Use \du+ to get additional information about each user, such as their description:
Now for the second way - we will use a SQL query to list the users in our database instances.
List Users in Postgres With a Query
The pg_user view of the pg_catalog schema under the postgres default database provides access to information about database users.
Launch the query below in a client supporting PostgreSQL, such as DbVisualizer, to get the list of all the users:
1
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;
The above Postgres list users query will return the following result:

Here’s what information each column of pg_catalog.pg_user contains:
Congrats! You just saw two effective ways to list users in Postgres.
Conclusion
In this article, you saw two different Postgres list users methods. As seen here, getting the list of users in a PostgreSQL server is a simple task. There are two methods to achieve that, and here we dug into both of them. The first involves a command-line command in psql, while the second requires a specific query.
To avoid using the CLI and better understand the result of your queries, you should adopt a powerful database client like DbVisualizer. This tool supports dozens of databases and comes with complete query optimization capabilities, a drag-and-drop UI to build queries, and ER schema representation functionality. Download DbVisualizer for free!
FAQ
How to list superusers in Postgres?
To list superusers in Postgres, you can query the pg_roles catalog table with a specific filter as follows:
1
SELECT *
2
FROM pg_catalog.pg_user
3
4
WHERE usesuper = true;
This will return only users with the SUPERUSER attribute.
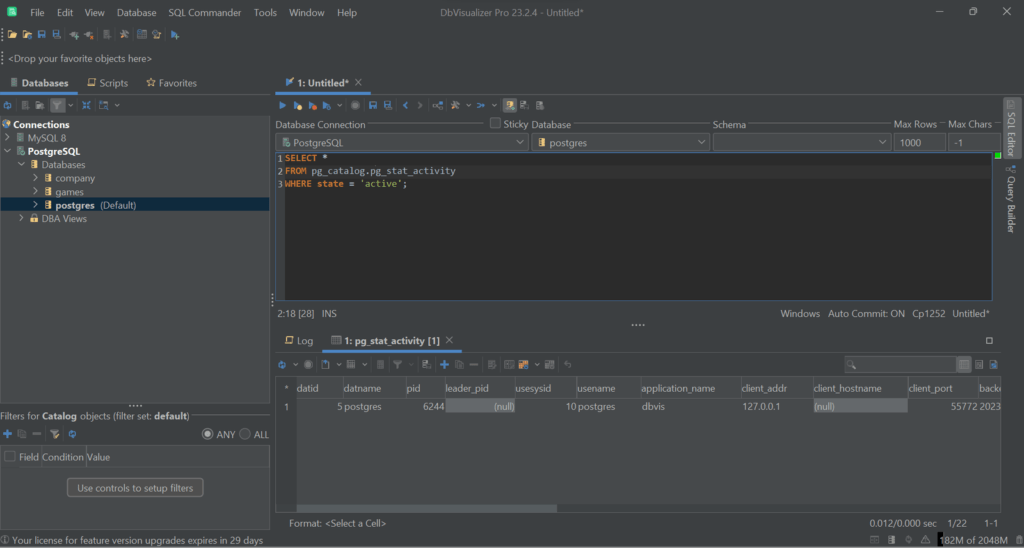
How to identify and list the currently logged-in users in a PostgreSQL database?
To identify and list the currently logged-in users in PostgreSQL, run the query below on the pg_catalog.pg_stat_activity system view:
1
SELECT *
2
FROM pg_catalog.pg_stat_activity
3
WHERE state = 'active';
What role does authentication play when listing users in PostgreSQL?
Authentication ensures security by verifying the identity of the user attempting to access user-related information. Thus, by enforcing authentication PostgreSQL restricts unauthorized access, contributing to secure user listing.
Is listing a large number of Postgres users fast?
The speed of listing numerous PostgreSQL users depends on various factors, including server performance, database size, and hardware resources. At the same time, it can be considered a fast operation as it involves a simple query on a system view.
What tools make it easier to list all users in Postgres?
A database client such as DbVisualizer provides a visual interface for executing queries. This tool offers SQL query execution capabilities, allowing you to run the "Postgres list users" query easily. In addition, it offers export functions, SQL history, and more to improve your PostgreSQL database management experience.