intro
Let’s explore the top database tools that every developer should know and leverage to optimize database management.
As a developer or database administrator, you know how challenging working with databases can be. Fortunately, you are not alone, as dozens of database tools have emerged over the years to support nearly every task in the database lifecycle.
In this guide, you will learn what these tools are, why they matter, and see a carefully compiled list of the best database tools for developers.
Let’s dive in!
What Is a Database Tool?
A database tool is any kind of software solution that helps you build, maintain, and interact with databases. In simpler terms, it can be a desktop application, command-line tool, cloud platform, web application, or similar solution that simplifies tasks such as data storage, management, logging, security, administration, and other data-related operations.
There are database tools for every step of the data lifecycle, supporting both SQL and NoSQL databases. These solutions can serve non-technical users as well as developers, but in this article, we will focus on the tools most relevant to developers.
Why Developers Need Specific Database Tools
Skilled developers and database administrators can certainly manage databases directly through the command line and by operating on the underlying servers. However, this approach is risky, complex, and time-consuming.
Specialized database tools support most day-to-day tasks, making it easier to handle everything from schema design and query optimization to monitoring and backups. They also help enforce structured processes, improve team collaboration, and reduce the risk of misconfigurations.
Beyond convenience, database tools for developers provide advanced features that boost performance, strengthen security, and optimize workflows. Thanks to them, developers can focus more on building applications and less on low-level database administration.
Top 10 Database Tools for Developers
Discover the most important and useful database tools that can help you take database management to the next level as a developer.
Disclaimer: This is not a ranking but rather a curated list of some of the best database tools for developers.
Database Clients
Database clients are applications, usually desktop-based, that allow developers to connect to and manage database servers. They provide graphical or command-line interfaces for tasks such as running queries, browsing data, and administering one or multiple database systems. These tools are essential for database development, debugging, and data manipulation.
Note: Some database clients include so many additional features (e.g., data import/export, backup management, SQL script handling, performance monitoring, version control, and more) that they can cover most of the tasks handled by other categories of database tools.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| DbVisualizer | Top-rated, multi-database client with broad JDBC support, visual ERDs, SQL editor, import/export capabilities, and many other features. |
| DataGrip | Commercial IDE by JetBrains for professional SQL developers. It supports 20+ databases with smart SQL editing and AI features. |
| DBeaver | Open-source + commercial, supports 100+ databases, visual query builder, ER diagrams, and cross-platform. |
| TablePlus | Proprietary client with clean interface, fast performance, supports multiple relational and some NoSQL DBs, including iOS app. |
| HeidiSQL | Free, lightweight Windows-only client. It is ideal for MySQL, MariaDB, PostgreSQL, and basic SQL management. |
Further reading:
Database Design and Modeling Tools
Database design in Lucidchart, one of the possible tools for this task
Database design and modeling tools help developers visually plan and structure a database before implementation. They enable the creation of diagrams like ERDs to map out tables, columns, and relationships. This is useful for guaranteeing a logical and normalized database structure to craft a blueprint for the final database.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Lucidchart | Cloud-based diagramming tool with ERD templates for collaborative database schema design. |
| draw.io | Open-source diagramming platform suitable for ERDs and general-purpose modeling across devices. |
| Luna Modeler | Desktop application focused on practical database modeling, including SQL scripting and reverse/forward engineering. |
| DbSchema | Desktop tool for SQL/NoSQL schema design with Git-based collaboration, documentation, and database synchronization. |
Further reading:
Database Version Control Tools

Version control tools track and manage changes to database schemas or SQL scripts, just like it happens in source code management. They allow teams to roll back updates, synchronize environments, and collaborate more efficiently. Using these tools prevents conflicts and ensures consistency across different environments.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Flyway | Open-source, database-agnostic migration tool using SQL scripts, easy to integrate into CI/CD pipelines. |
| Liquibase | Open-source, vendor-agnostic tool using “changesets” in XML, YAML, JSON, or SQL. |
| Sqitch | Database change management tool for tracking, deploying, and reverting schema changes in a version-controlled way. |
| DVC (Data Version Control) | Open-source tool that integrates with Git to version data files and ML models for reproducible workflows. |
Further reading:
Database Backup and Recovery Tools

These tools automate the process of backing up databases and restoring them or their data when needed. They protect against data loss due to hardware failures, human error, or cyberattacks. Backup and recovery tools provide peace of mind, opening the door to point-in-time recovery. They support developers in maintaining business continuity with minimal disruption.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| pg_dump + pg_restore | PostgreSQL tools for full or partial backups and restores. |
| mysqldump | MySQL/MariaDB tool to export and restore databases via SQL scripts. |
| Percona XtraBackup | Open-source hot backup for MySQL/MariaDB. It is non-blocking for large DBs. |
| Bacula | Enterprise backup for multiple DBs. It supports scheduling and encryption. |
| Veeam Backup & Replication | Commercial DB/server backup. It supports SQL Server, Oracle, and cloud DBs. |
Further reading:
Database Performance Tools
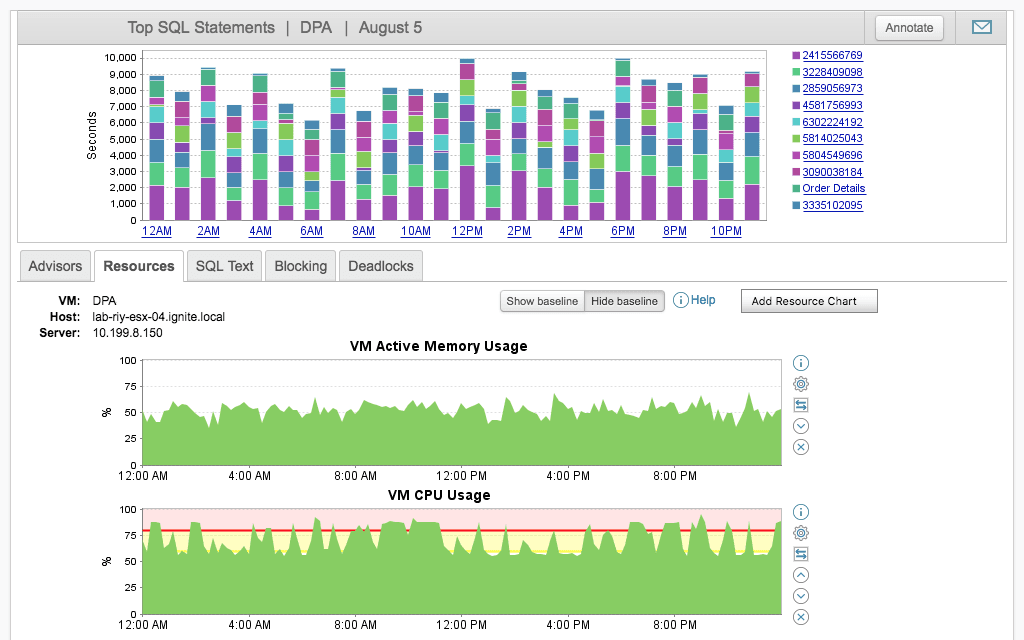
Performance tools monitor database operations, providing insights to optimize query execution, indexing, and resource usage. They help developers identify bottlenecks, tune queries, and maintain fast response times. These tools are essential for keeping applications responsive and scalable, even under heavy workloads.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| SolarWinds DPA | Commercial tool for monitoring and analyzing SQL Server, Oracle, and MySQL. |
| New Relic | Cloud-based performance monitoring for databases and applications. |
| Percona Monitoring & Management (PMM) | Open-source monitoring for MySQL, MongoDB, and PostgreSQL performance. |
| Datadog | Monitoring platform with real-time query profiling and execution analysis. |
Further reading:
Database Testing Tools

Database testing tools simulate real-world database interactions and validate data integrity, query results, and transaction behavior. They can automate various tests, including functional, load, and security testing, to make sure data is accurate and the system can handle expected workloads. Their goal is to help developers identify bugs in database architecture, queries, SQL procedures, etc.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| tSQLt | Unit testing framework for SQL Server. It can run tests directly in SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio). |
| DBUnit | JUnit extension for unit and integration testing of database-driven apps. |
| DbFit | Open-source, script-based tool for automated database testing across multiple databases.. |
| NoSQLUnit | JUnit extension for testing applications using NoSQL databases. |
Database CI/CD Tools

A database CI/CD pipeline built with Airbyte, one of the top solutions for the task
CI/CD tools automate the integration of database changes into the application development and deployment pipeline. They support the continuous delivery of database updates by automating testing, integration, and deployment processes. This helps teams release new features faster, while maintaining databases updated across all environments.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Airbyte | Open-source data integration platform for CDC and bulk data loading, known for extensibility and real-time synchronization. |
| Apache Kafka | Distributed event streaming platform designed for high-throughput, low-latency real-time data pipelines and analytics. |
| Confluent | Commercial, enterprise-ready version of Apache Kafka that adds managed services and easier data pipeline management. |
Further reading:
Database Logging Tools

Logging tools capture database operations, errors, and access events for monitoring, compliance, or debugging. They provide insights into usage patterns, help detect anomalies, and assist in troubleshooting issues quickly. By maintaining detailed records, logging tools also support database accountability.
Examples:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Splunk | Platform for collecting, indexing, and analyzing logs, offering real-time visibility and search. |
| pgBadger | PostgreSQL log analyzer that generates performance reports and insights. |
| ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) | Open-source log management trio: Logstash processes data, Elasticsearch indexes it, Kibana visualizes it. |
| Fluentd | Open-source log collector that unifies and routes logs from multiple sources. |
Database Tool Builder Solutions
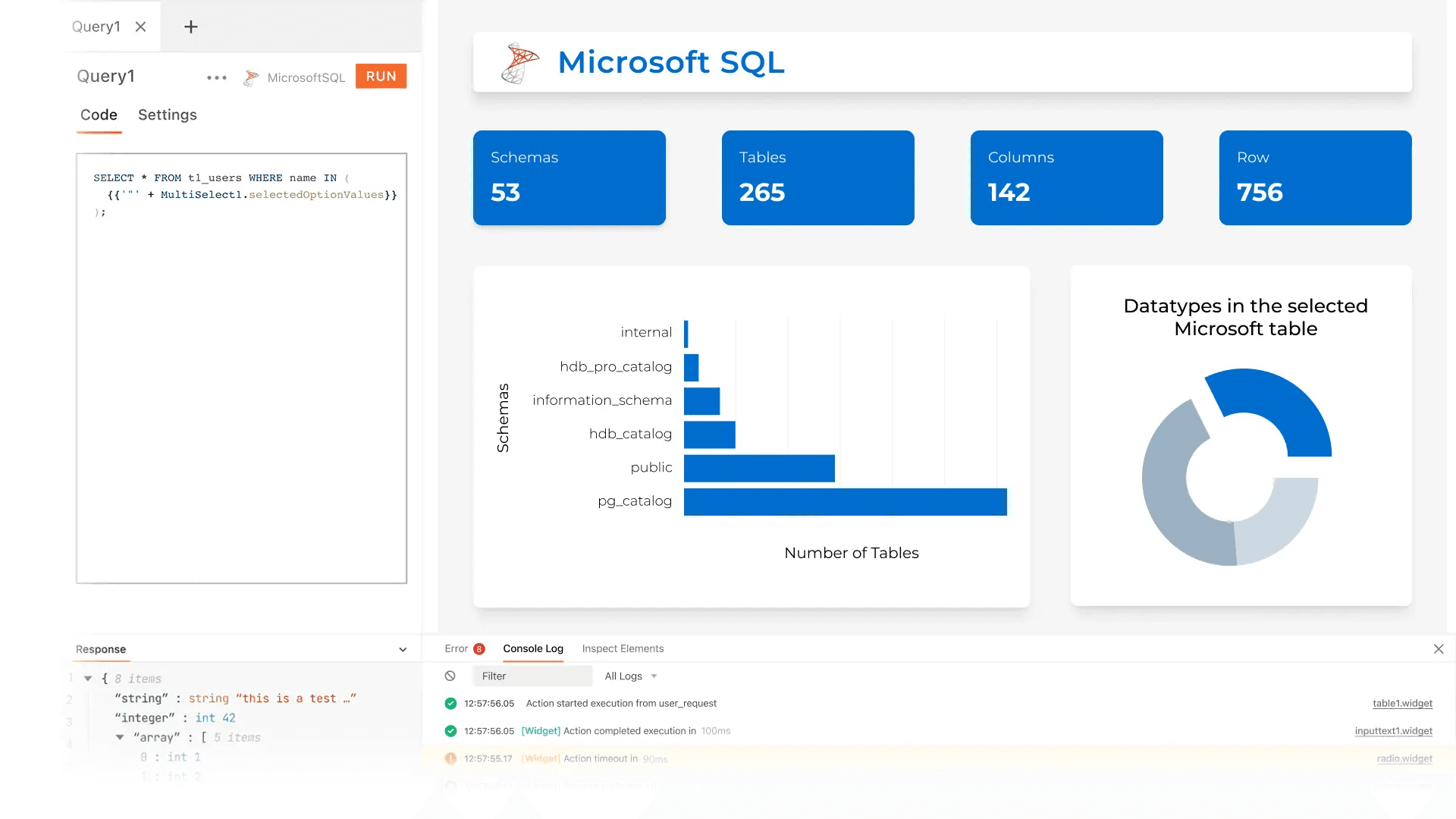
Database tool builders are platforms, typically low-code or no-code, that help developers quickly create custom applications. They rely on prebuilt components to speed up the development of internal tools, admin panels, dashboards, and mocks built around particular business needs.
Examples:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Appsmith | Open-source low-code platform for building dashboards, admin panels, and internal apps with SQL database integration. |
| DronaHQ | Low-code platform with drag-and-drop UI and visual SQL query builder for creating internal tools and workflows. |
| Google AppSheet | No-code platform to build mobile and web apps from SQL databases and other data sources without writing code. |
| Microsoft Power Apps | Low-code platform for creating custom business apps that connect to SQL Server and other data sources. |
| Softr | No-code platform for quickly building web apps and internal tools using SQL databases and other data sources. |
Further reading:
Database Security Tools
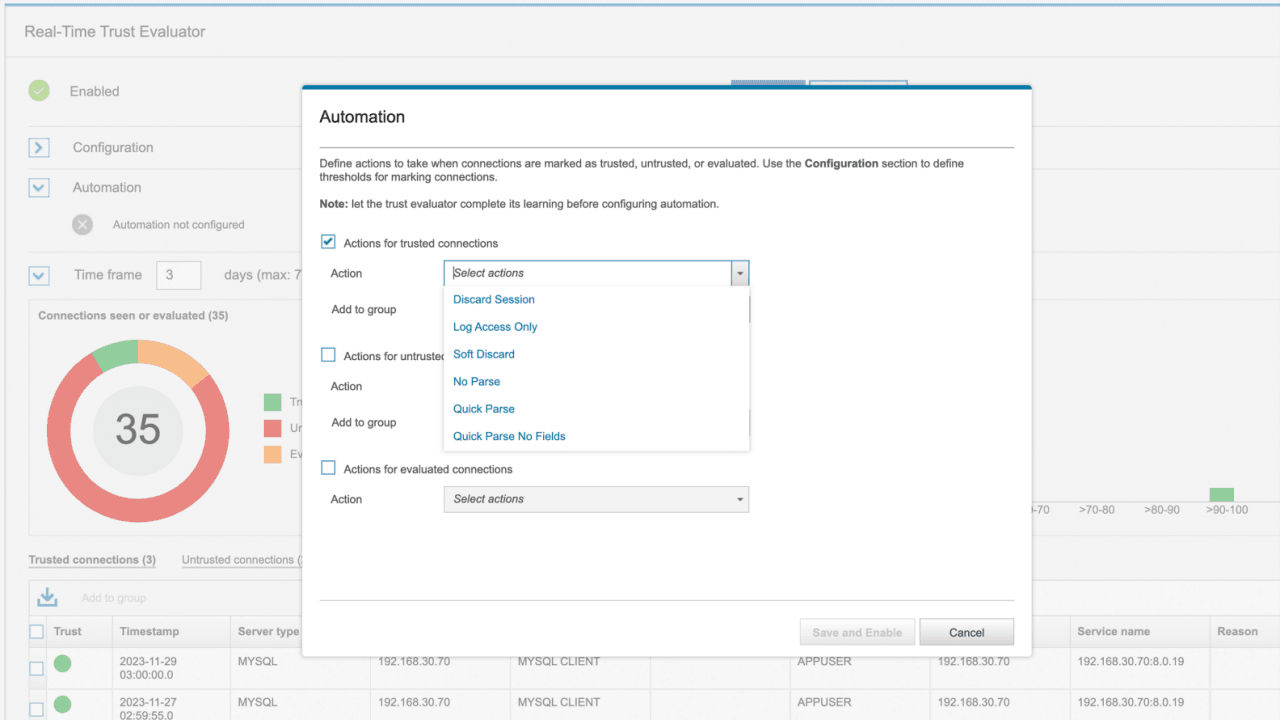
SQL protection with IBM Guardium, one of the top enterprise tools for database security
These security tools are designed to protect databases by preventing unauthorized access, breaches, and data corruption. They enforce policies that help developers and security teams safeguard sensitive information, ensure regulatory compliance, and minimize the risk of costly security incidents.
Examples:
| Tool | Short Description |
|---|---|
| IBM Guardium | Enterprise-grade monitoring, vulnerability assessment, and encryption for hybrid cloud databases. |
| Fail2ban | Open-source intrusion prevention tool that blocks IPs after repeated failed logins. It is configurable for databases. |
| Imperva Data Security | Monitors, audits, and detects threats in real time. It enforces policies and protects sensitive data. |
| Oracle Audit Vault and Database Firewall | Monitors Oracle DB activity and blocks unauthorized SQL to prevent attacks. |
| SQLMap | Automated tool for detecting and testing SQL injection vulnerabilities. |
Further reading:
Conclusion
In this blog post, you learned what database tools are, why developers need them, and reviewed a selection of some of the best solutions for database management available today. To get the most out of them, it is best to combine a set of complementary tools in a best-of-breed approach.
Although no single tool can handle every task, some feature-rich database clients come close. This is why it makes sense to choose a powerful, versatile client like DbVisualizer, a top-rated database tool with over 7 million downloads worldwide that has been supporting developers since 1999.
Do you think we missed any specific tool or want to collaborate in the future, we would love to hear from you!
FAQ
What are the types of developer database tools?
Database tools for developers can be classified in several ways, depending on multiple aspects. They may be open-source or commercial, visual or command-line based, and support no-code or low-code workflows. Some focus on database design, while others handle administration, migration, monitoring, or security. Tools can also vary in scope, supporting a specific database or multiple database systems. As a result, there is no single, universal classification system.
Is it better to rely on open-source database tools or commercial database tools?
Both open-source and commercial database tools have their strengths. Developers tend to prefer open-source database tools for solutions that run directly on your servers, such as security or monitoring system, as you want full transparency.
Commercial tools usually offer intuitive user interfaces, dedicated support, and advanced features that help developers in enterprises or large teams save time. The right choice depends on your project’s requirements, your team’s expertise, and whether you value control over convenience and support.
Where can I find a curated list of awesome database tools?
If you are looking for a curated, up-to-date, and community-maintained list of database tools, refer to the “Awesome Database Tools” GitHub repository. This boasts over 4.7k stars and features more than 100 tools, making it a valuable resource for developers seeking recommended database solutions.