intro
Let’s explore the most useful tools for database administrators, carefully selected and compared in a curated list!
DBAs carry uptime, performance, and security on their shoulders. This guide links your daily tasks to the right tools, with quick notes on how DbVisualizer goes beyond ad hoc querying.
Dive into a practical, category-by-category guide to the best tools for database administrators, covering SQL clients, monitoring, backups, migrations, security, and automation!
What is a Database Administration Tool?
A database administration tool is any application that helps DBAs manage database engines and data safely and efficiently. That includes tools for observability and alerting, performance diagnostics, security controls, backup and disaster recovery, schema versioning and migration, data movement, and automation.
Why DBAs Need a Diverse Toolkit
Production data systems demand:
In simpler terms, given all these requirements, database administrators should not be left to work alone but supported by the right tools. Time to analyze the tools that cover those needs, organized by category.
Top Database Tools for Administrators
Explore a list of database tools optimized and targeted for DBAs, organized by category.
Note: Categories may overlap. Choose the tools that best match your database engines and hosting model, whether self-managed or cloud
1. SQL Clients and Admin Consoles
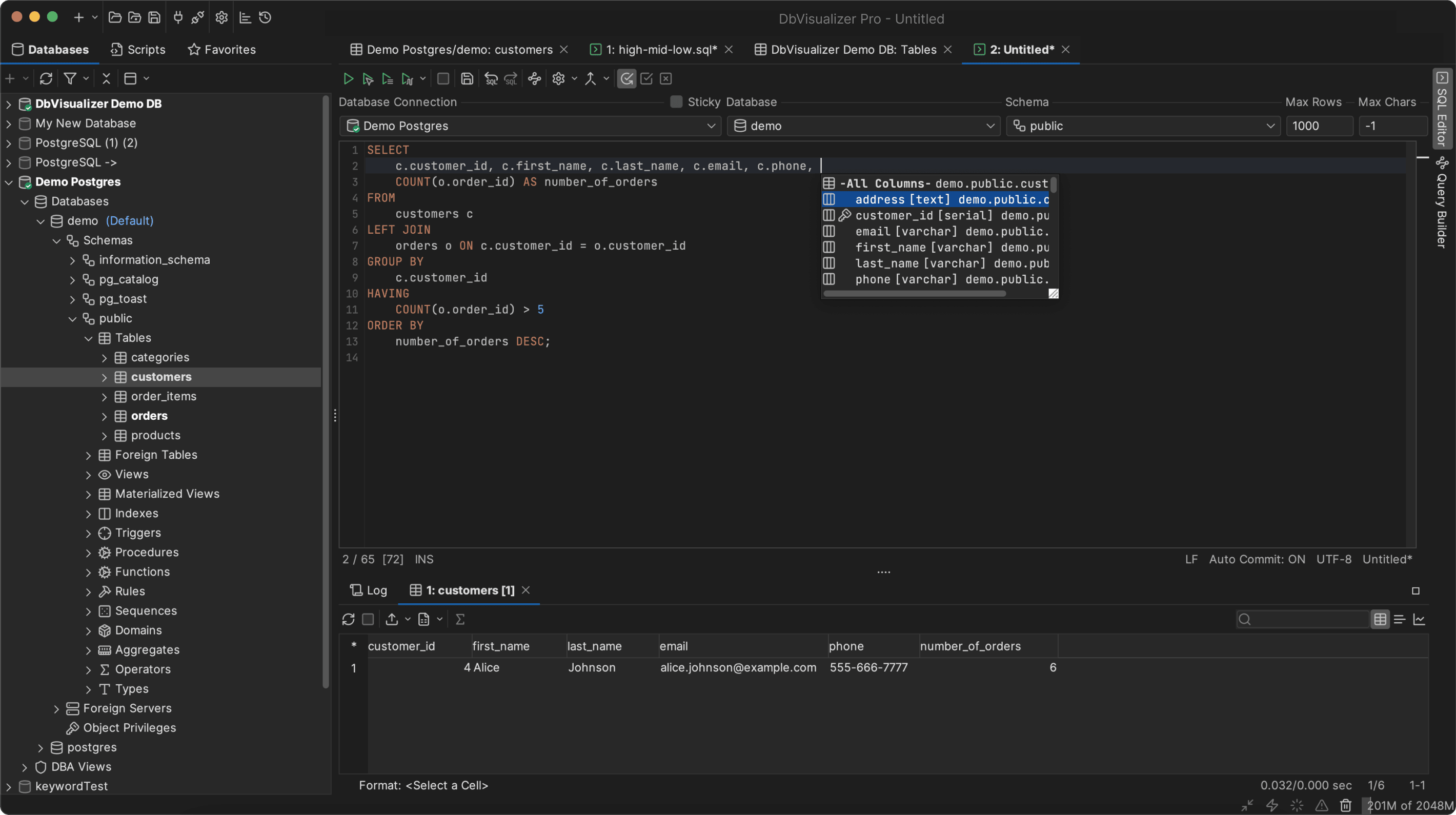
Your command center for connecting, inspecting schemas, running diagnostics, and making controlled changes.
Examples:
| Tool | Why DBAs use it |
|---|---|
| DbVisualizer | Universal SQL client across many engines via JDBC with SSH tunneling, object browser for tables, indexes, constraints and users, visual query builder, references and ER graphs, explain or explain plan where supported, in place data editing, bulk export and import, result set charts, monitors for auto refreshing key queries, and built in Git to version scripts and runbooks. |
| DataGrip | Commercial IDE with smart code assistance and multi engine introspection. |
| DBeaver | Open source plus enterprise editions with wide driver support and ER diagrams. |
| SSMS or Azure Data Studio | Deep SQL Server tooling including plan analysis via extensions. |
| pgAdmin | Native PostgreSQL console. |
| MySQL Workbench | Native MySQL design and admin features. |
If you want one cross database console that also helps with day to day analysis, DbVisualizer is a solid default that scales from quick fixes to repeatable runbooks.
Further reading:
2. Monitoring and Observability

Keep tabs on availability, errors, throughput, latency, locks, and resource usage.
Examples:
| Tool | Focus |
|---|---|
| Percona Monitoring and Management | Open source monitoring for MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. |
| Datadog, New Relic, Dynatrace | Cross stack observability with database deep dives and alerting. |
| pganalyze | Postgres plans, wait analysis, and index advice. |
| Redgate SQL Monitor or SolarWinds DPA | SQL Server focused monitoring and blocking or deadlock insights. |
| Cloud vendor tools | RDS or CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, Cloud Monitoring for managed services. |
For lightweight checks, you can keep a few health queries in DbVisualizer and use monitors to auto refresh them during incidents or maintenance windows.
Further reading:
3. Performance Tuning and Query Analysis
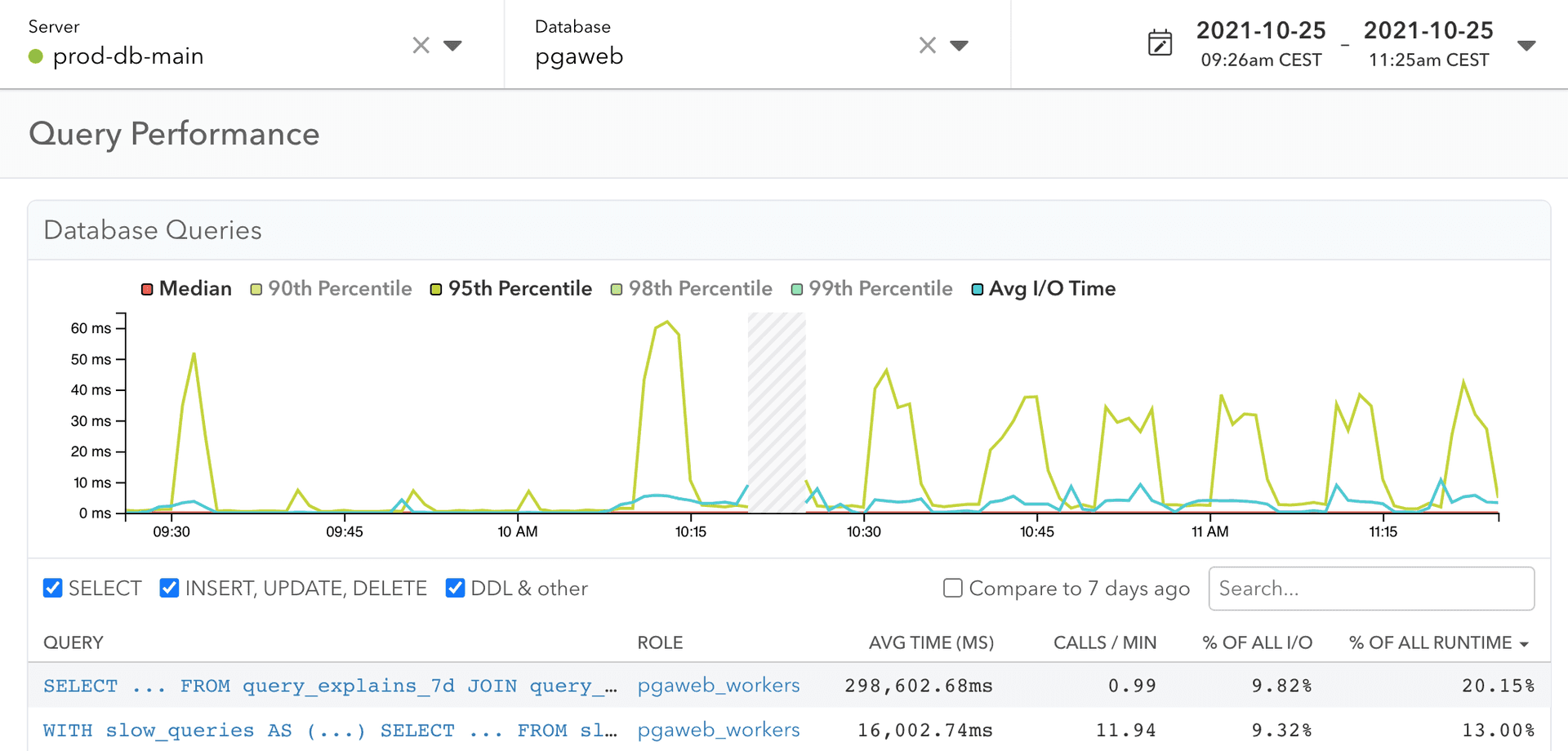
Drill into query plans, wait events, indexes, and caches to remove bottlenecks.
Examples:
| Tool | Strength |
|---|---|
| Native engine tools | Postgres EXPLAIN and pg_stat views, SQL Server Query Store and DMVs, MySQL Performance Schema, Oracle AWR or ASH. |
| pganalyze, pgMustard, pgBadger | Specialized Postgres analysis and reporting. |
| SQL Sentry | Plan exploration and server side performance for SQL Server. |
You can optimize queries directly in DbVisualizer with explain or explain plan, references graphs for cardinality intuition, and before or after benchmarks versioned in Git.
Further reading:
4. Backup, Restore, Replication, and Disaster Recovery

Design for correct RPO (Recovery Point Objective) and RTO (Recovery Time Objective) with robust backups, tested restores, and resilient replication.
Examples:
| Tool | Use case |
|---|---|
| Percona XtraBackup | Hot backups for MySQL or InnoDB. |
| pgBackRest, Barman, WAL G | PostgreSQL backup and WAL management. |
| Oracle RMAN | Enterprise backup and recovery. |
| SQL Server native backups | Full, diff, and log with Agent or maintenance plans. |
| Patroni, Pacemaker, Always On | HA orchestration for Postgres and SQL Server. |
Further reading:
5. Security, Secrets, and Compliance

Manage users, roles, policies, encryption, secrets, and auditing.
Examples:
| Tool | Focus |
|---|---|
| HashiCorp Vault or cloud KMS | Secret management and key rotation. |
| Native IAM | AWS IAM with RDS, Azure AD for SQL, GCP IAM bindings. |
| Data masking and governance | Redgate Data Masker, Immuta, Privacera. |
| Auditing | Native audit logs with SIEM ingestion. |
Further reading:
6. Schema Versioning and Change Management
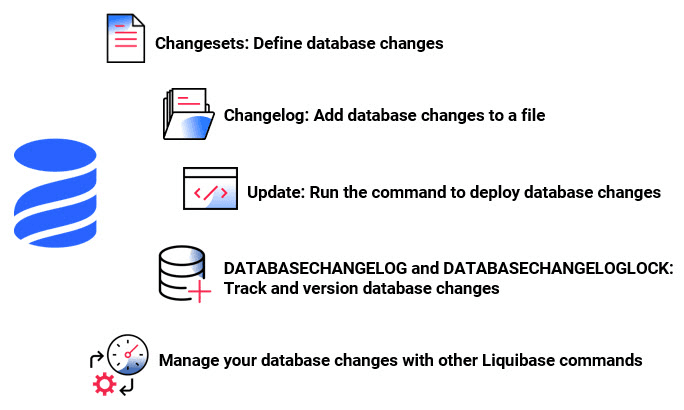
Make DDL (Data Definition Language) changes reproducible and reviewable.
Examples:
| Tool | What it does |
|---|---|
| Liquibase, Flyway | Declarative schema migrations with rollbacks and CI or CD hooks. |
| Redgate Change Automation | Version controlled deployments for SQL Server. |
| Alembic | App driven migrations for Python stacks. |
If you prefer not to add a separate migration tool for a small footprint, you can still keep admin SQL versioned in Git inside DbVisualizer and use its CLI to run scripts in your scheduler.
Further reading:
7. Data movement, CDC, and Migrations
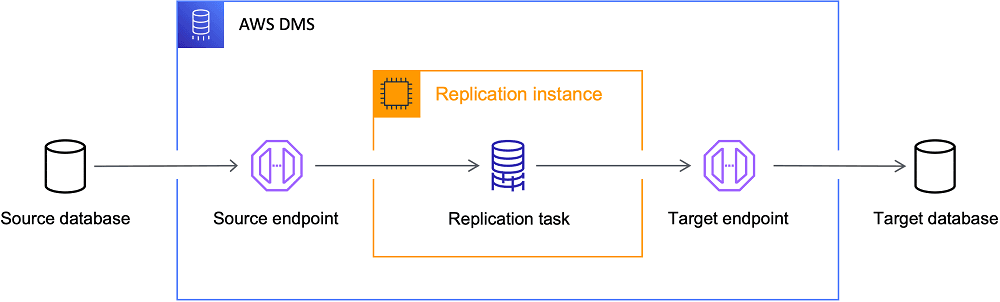
Move data reliably with batch or change data capture.
Examples:
| Tool | Use case |
|---|---|
| AWS DMS, Azure DMS, Google DMS | One time or continuous migrations into managed services. |
| Debezium | Open source CDC on Kafka for Postgres and MySQL. |
| Oracle GoldenGate, SharePlex | Enterprise replication and CDC. |
| Ora2Pg | Oracle to Postgres migrations. |
Further reading:
8. Automation and Runbooks
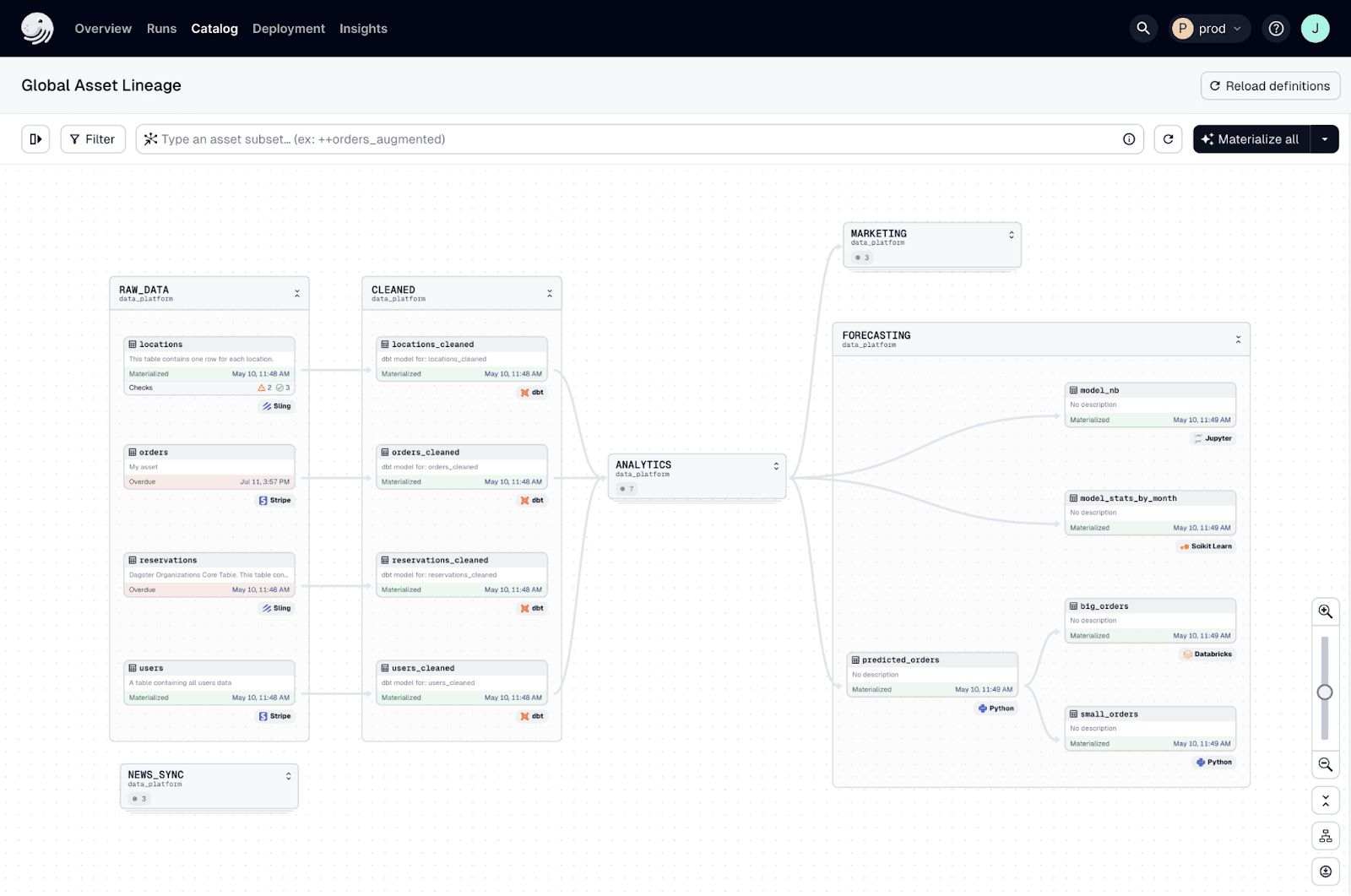
Dagster, an automation tool you can also use with databases
Codify repetitive tasks so they are repeatable, tested, and observable.
Examples:
| Tool | Strength |
|---|---|
| Ansible or Terraform | Provisioning, parameter changes, and infra as code. |
| Airflow, Dagster, Prefect | Job scheduling and dependency management. |
| Rundeck | Self service operations with approvals. |
For small jobs, you can generate command line scripts in DbVisualizer and run them from cron or your scheduler. Keep the SQL and shell together in Git for review.
Further reading:
9. Cloud Admin and Cost Control
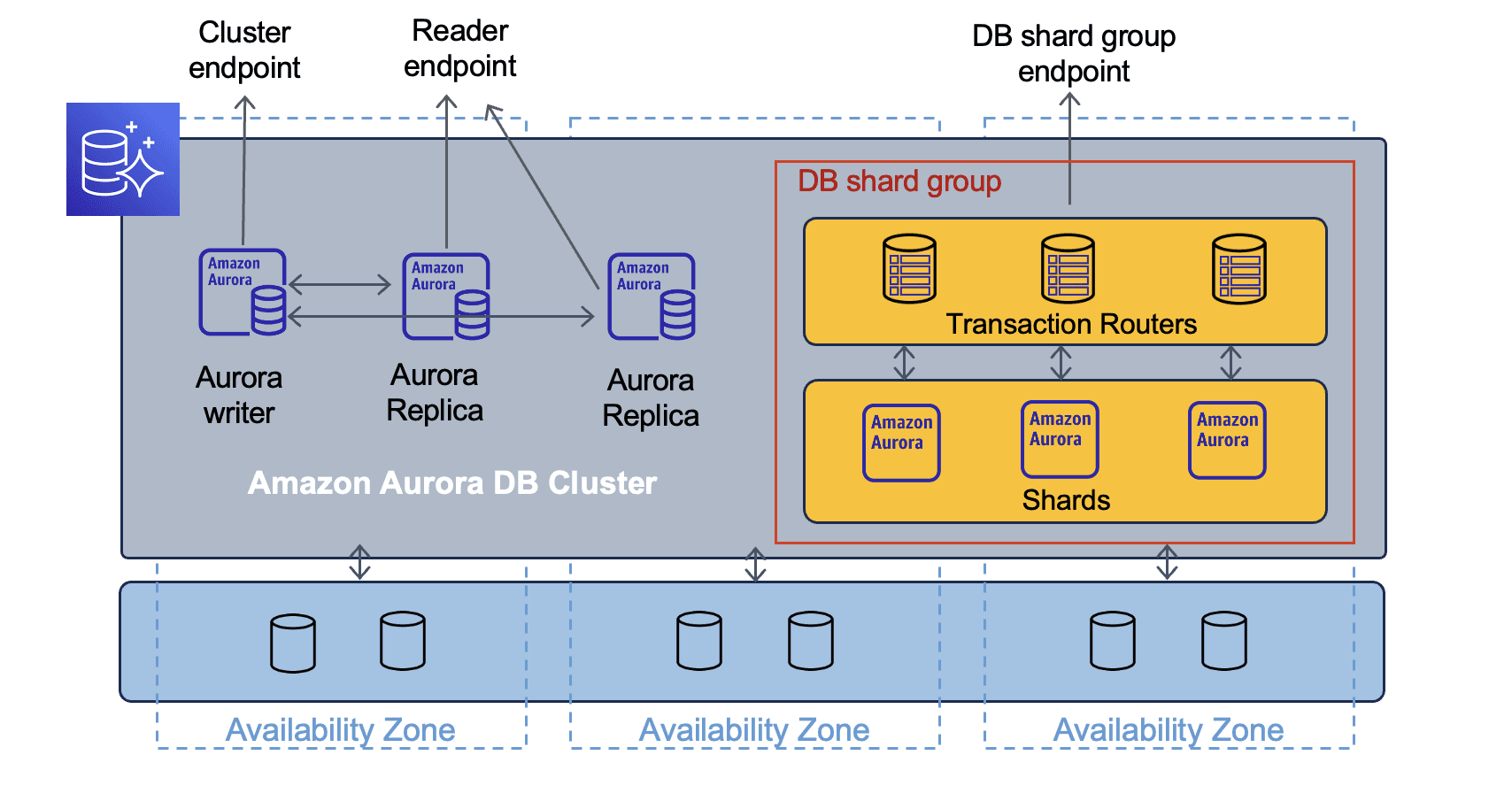
If you run managed services, master the consoles and the cost levers.
Examples:
| Platform | Admin focus |
|---|---|
| AWS RDS or Aurora | Instance sizing, storage autoscaling, snapshots, parameter groups, performance Insights. |
| Azure SQL or SQL MI | Elastic pools, failover groups, automatic tuning, alerts. |
| GCP Cloud SQL or AlloyDB | Maintenance windows, read replicas, high availability. |
| Snowflake | Roles and warehouses, resource monitors, query history, auto suspend. |
Further reading:
10. Documentation, Diagrams, and Knowledge
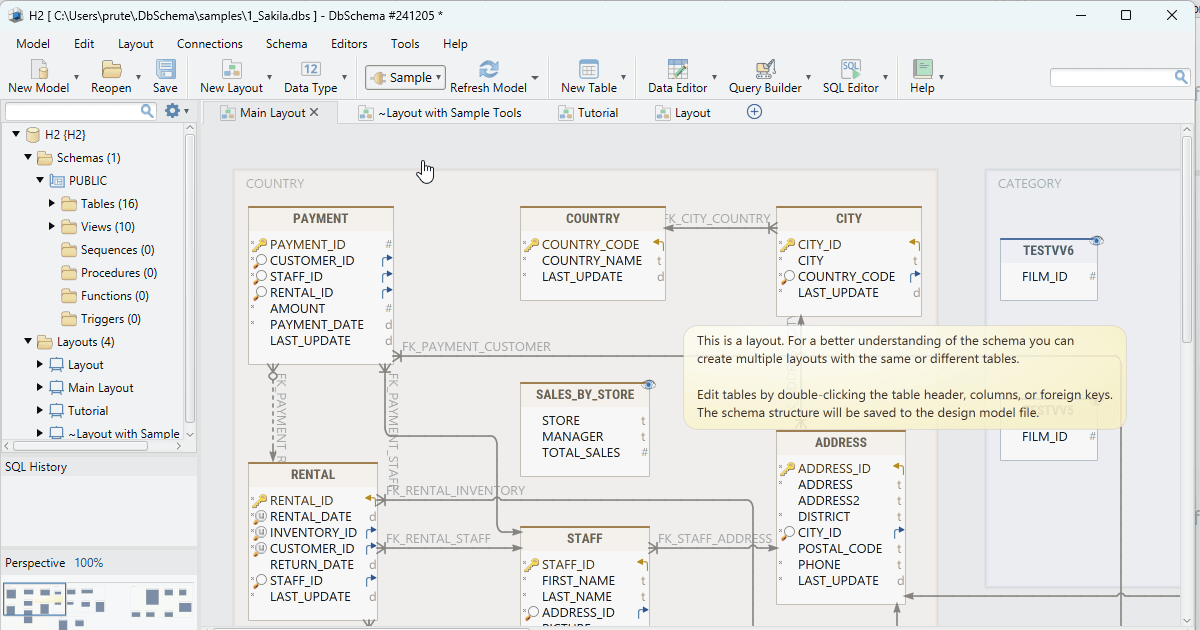
Good docs turn one time heroics into a system the team can run.
Examples:
| Tool | What it adds |
|---|---|
| DbVisualizer | Auto generated references and ER graphs to document relationships. Keep annotated SQL in Git as living runbooks. |
| DbSchema, ERwin, ER or Studio | Deep modeling, documentation, reverse engineering. |
| Confluence, Notion | Runbooks, incident retros, SOPs. |
| OpenMetadata, Atlan | Catalogs, ownership, and lineage for cross team clarity. |
Further reading:
Conclusion
A reliable admin stack pairs a universal SQL client with strong monitoring, repeatable change management, and tested backup and recovery. For everyday cross database work, DbVisualizer is a practical choice. It centralizes connections, clarifies schemas with ER graphs, helps tune with explain plan, keeps lightweight monitors running, and integrates with Git and a CLI so your operational SQL is reviewable and automatable.
Do you think we missed any specific tool or want to collaborate in the future? We would love to hear from you!
FAQ
What are the essential categories of DBA tools?
At minimum: SQL client or admin console, monitoring and observability, performance tuning, backup and disaster recovery, schema versioning, security and compliance, migration and CDC, automation, and documentation.
Which tool should I start with if I am a solo DBA?
Start with a universal SQL client, add PMM or a hosted monitor for your primary engine, and adopt Liquibase or Flyway for controlled schema changes. Layer in backup tooling that matches your RPO and RTO.
Can a SQL client replace a monitoring suite?
No, it cannot. A client like DbVisualizer is great for ad hoc checks and lightweight monitors, but production systems need server side metrics, alerting, and retention from a real observability stack.
How do I keep database changes safe?
Use migrations in version control, peer review with pull requests, tagged releases, and a rollback plan through backups or down migrations. Test in staging, then promote.